Carbon atoms are the building blocks of life. They play a crucial role in organic chemistry and are found in everything from simple molecules like carbon dioxide to complex structures like DNA. Representing these atoms visually is essential for students, scientists, and educators alike to understand their properties and interactions. Whether it's a 3D model or a simple diagram, visualizing carbon atoms helps us grasp complex concepts more easily.
Understanding the Structure of Carbon Atoms
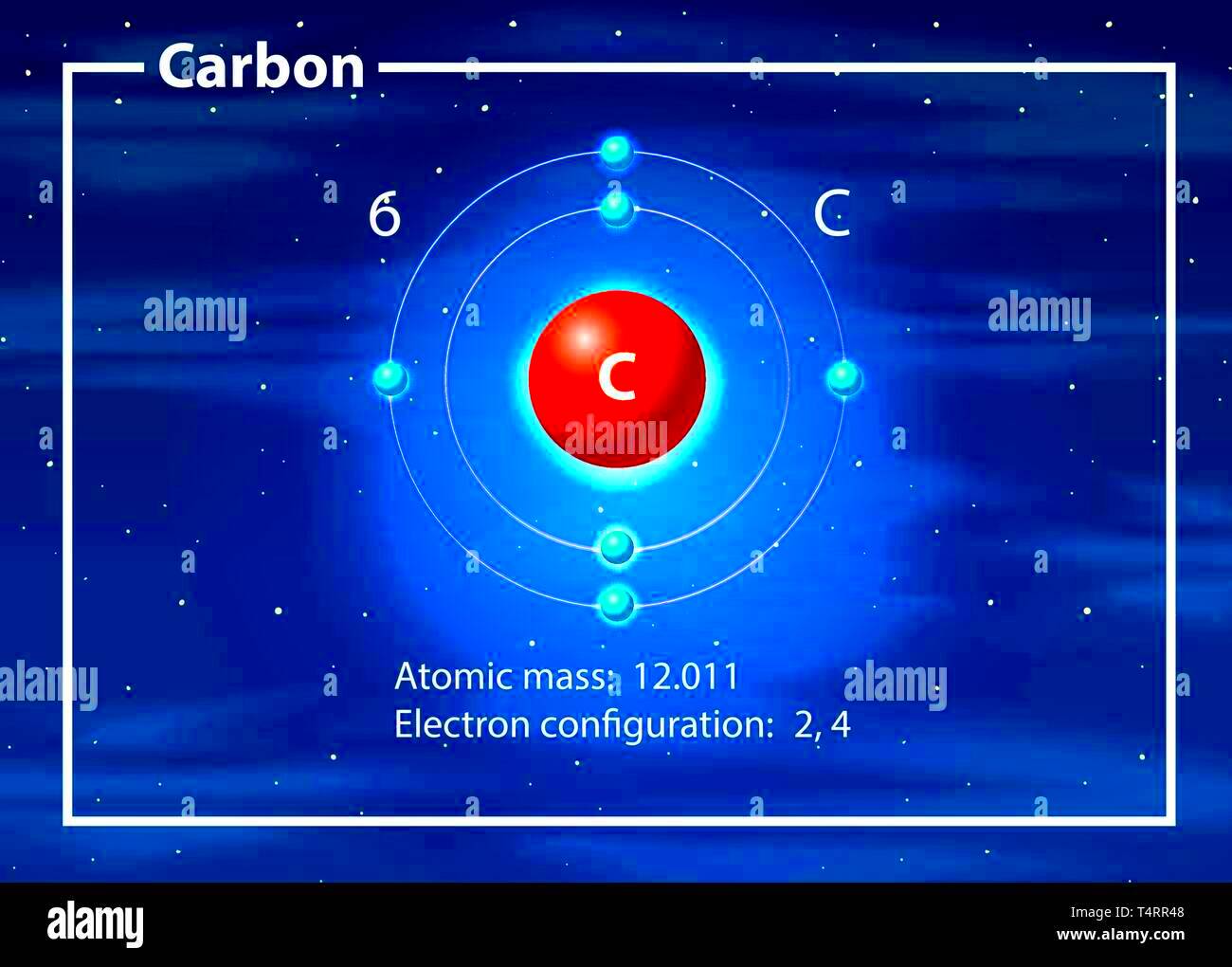
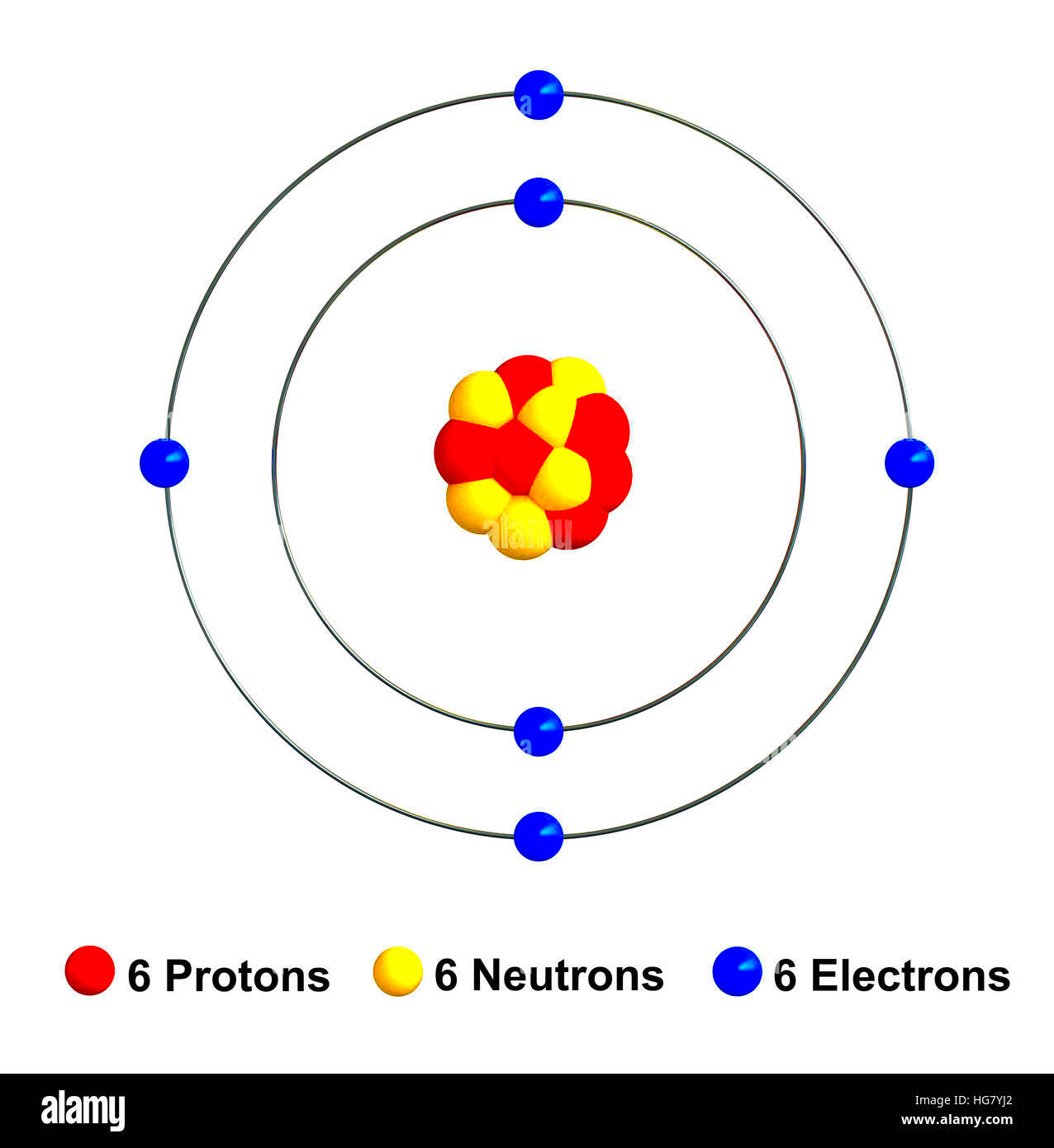
Carbon atoms have a unique structure that makes them essential to life on Earth. At the core of a carbon atom is a nucleus containing six protons and six neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are six electrons, arranged in two energy levels. The first energy level holds two electrons, while the second holds four, which allows carbon to form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
The ability of carbon to bond with so many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and itself, makes it versatile in forming a wide variety of compounds. This bonding property is key to creating large molecules like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Here's a simple breakdown of a carbon atom's structure:
- Protons: 6
- Neutrons: 6
- Electrons: 6
- Electron Shells: 2 shells (2 electrons in the first, 4 in the second)
Also Read This: How to Remove the Alamy Watermark with Photoshop: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Importance of Representing Carbon Atoms in Scientific Visuals
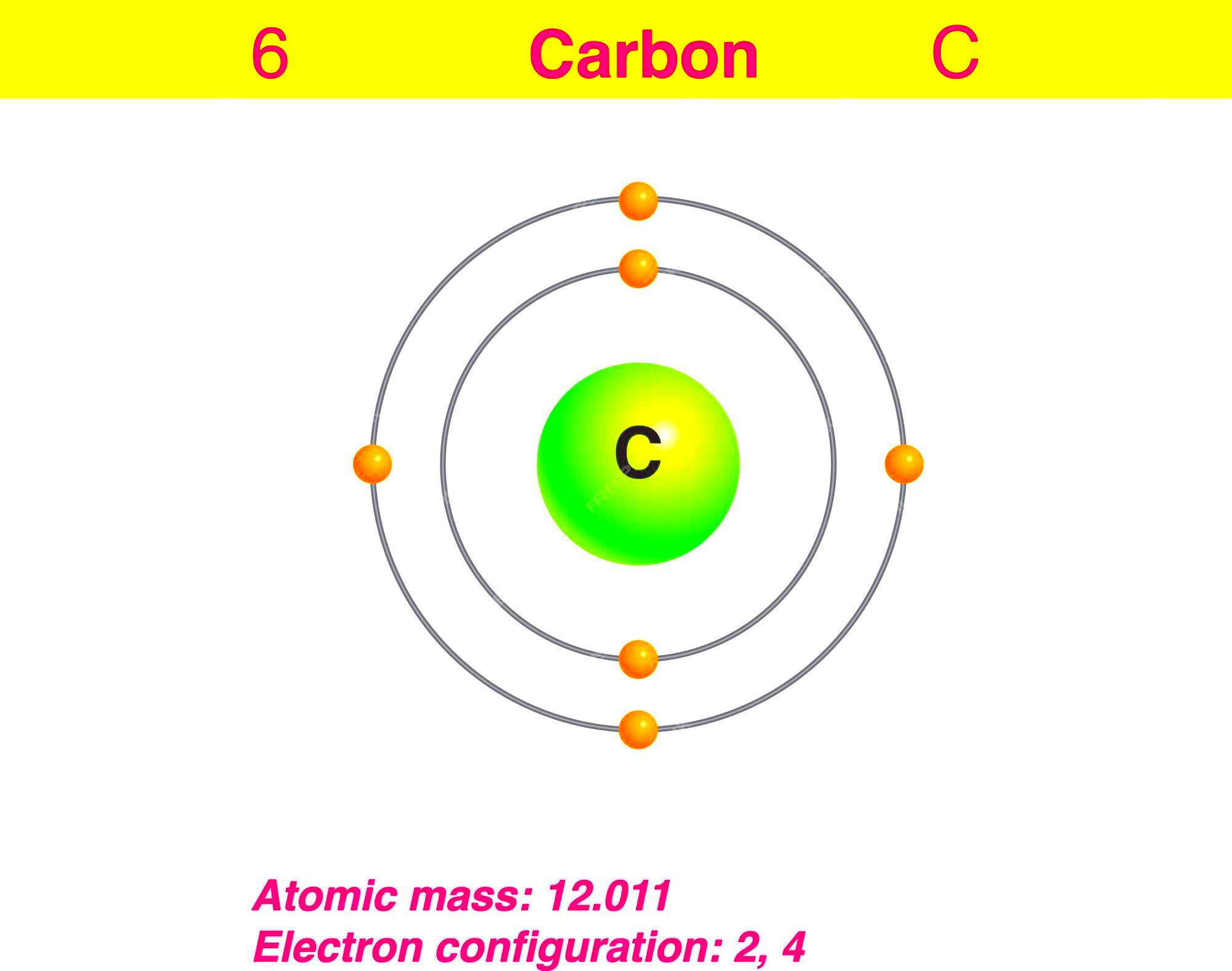
Visual representations of carbon atoms are essential for communicating scientific concepts. They simplify complex topics, making them easier to understand, especially for students and professionals learning new ideas. By seeing how carbon atoms bond and interact with other elements, we can better comprehend chemical reactions and molecular structures.
Here are some reasons why representing carbon atoms visually is so important:
- Educational Value: Visuals provide a clear way to teach concepts like bonding, molecular shapes, and reactions.
- Accuracy: Diagrams and 3D models ensure accurate representation of the atom's structure.
- Enhanced Learning: A picture is worth a thousand words—visual aids can make abstract concepts easier to grasp.
- Practical Application: Scientists use visuals to design new molecules, understand reactions, and create new materials.
These visual representations help bridge the gap between abstract theory and practical application, making the study of carbon atoms more accessible to everyone.
Also Read This: Top Strategies to Increase Discoverability on Alamy Stock Photos
Different Methods of Representing Carbon Atoms
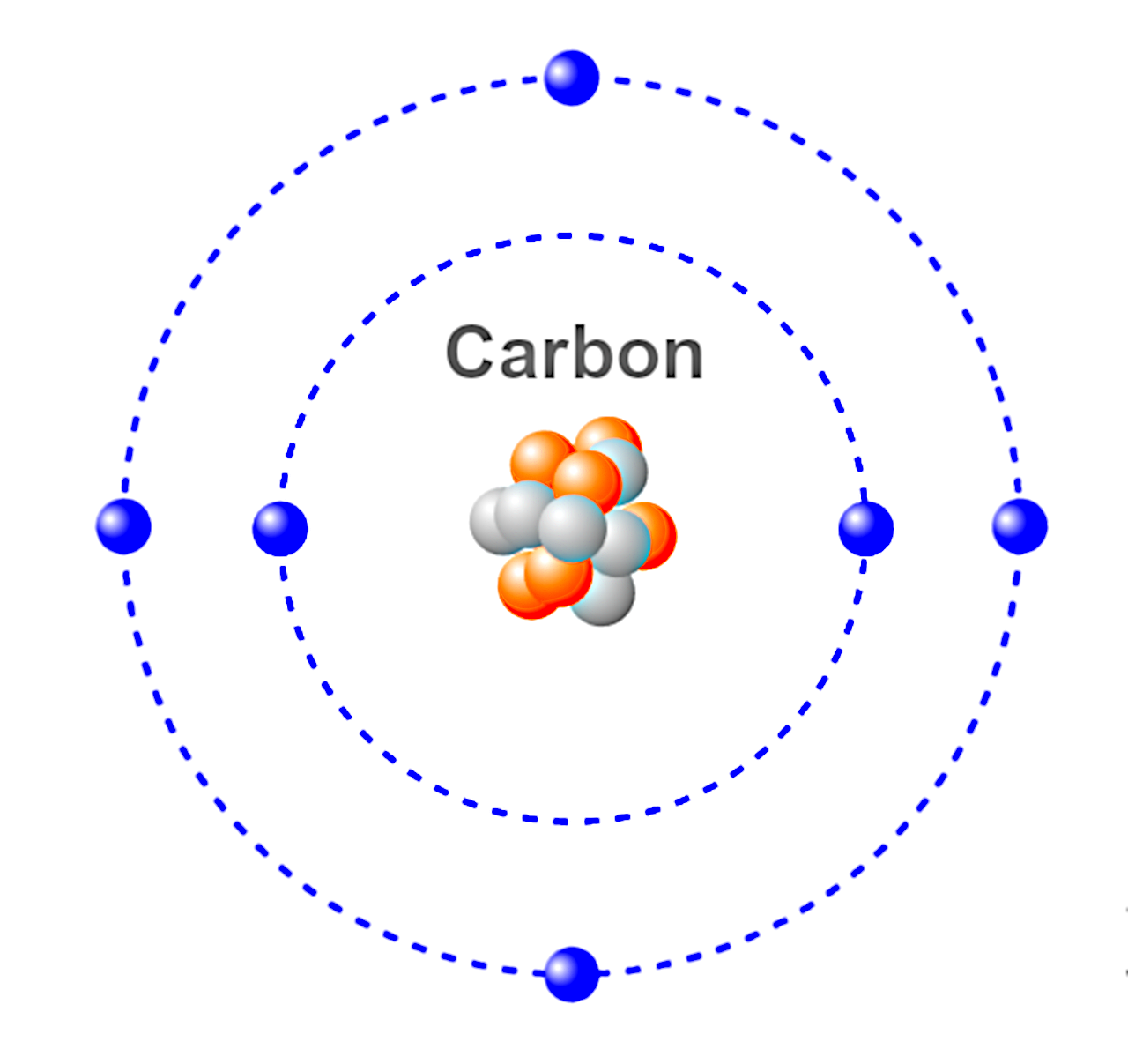
There are several ways to represent carbon atoms, each designed to highlight different aspects of their structure and bonding. Whether in 2D drawings or 3D models, these representations help clarify how carbon atoms interact with other elements. Let's look at some common methods:
- Ball-and-Stick Model: This is one of the most popular ways to represent atoms. In this model, the carbon atom is depicted as a sphere (the ball), and the bonds between atoms are represented by sticks connecting the spheres. This model highlights the geometry of molecules and the bond angles between atoms.
- Space-Filling Model: Unlike the ball-and-stick model, this model represents atoms as spheres whose size corresponds to their actual size. The spheres are packed together, giving a more accurate picture of the molecule’s overall shape.
- Lewis Dot Structures: These are simplified representations where dots around an element symbol represent valence electrons. For carbon, four dots are placed around the "C" symbol to show its ability to form four bonds.
- 3D Molecular Models: These models use software to create a digital, interactive representation of a carbon atom and its bonds. They allow users to rotate and zoom in on molecular structures, providing a more dynamic and accurate view.
Each of these methods has its uses depending on the context. For example, the ball-and-stick model is great for understanding molecular geometry, while 3D models are perfect for visualizing more complex interactions in real-time.
Also Read This: Alamy vs Shutterstock: Which Stock Photography Platform is the Best?
Tools and Software Used for Visualizing Carbon Atoms
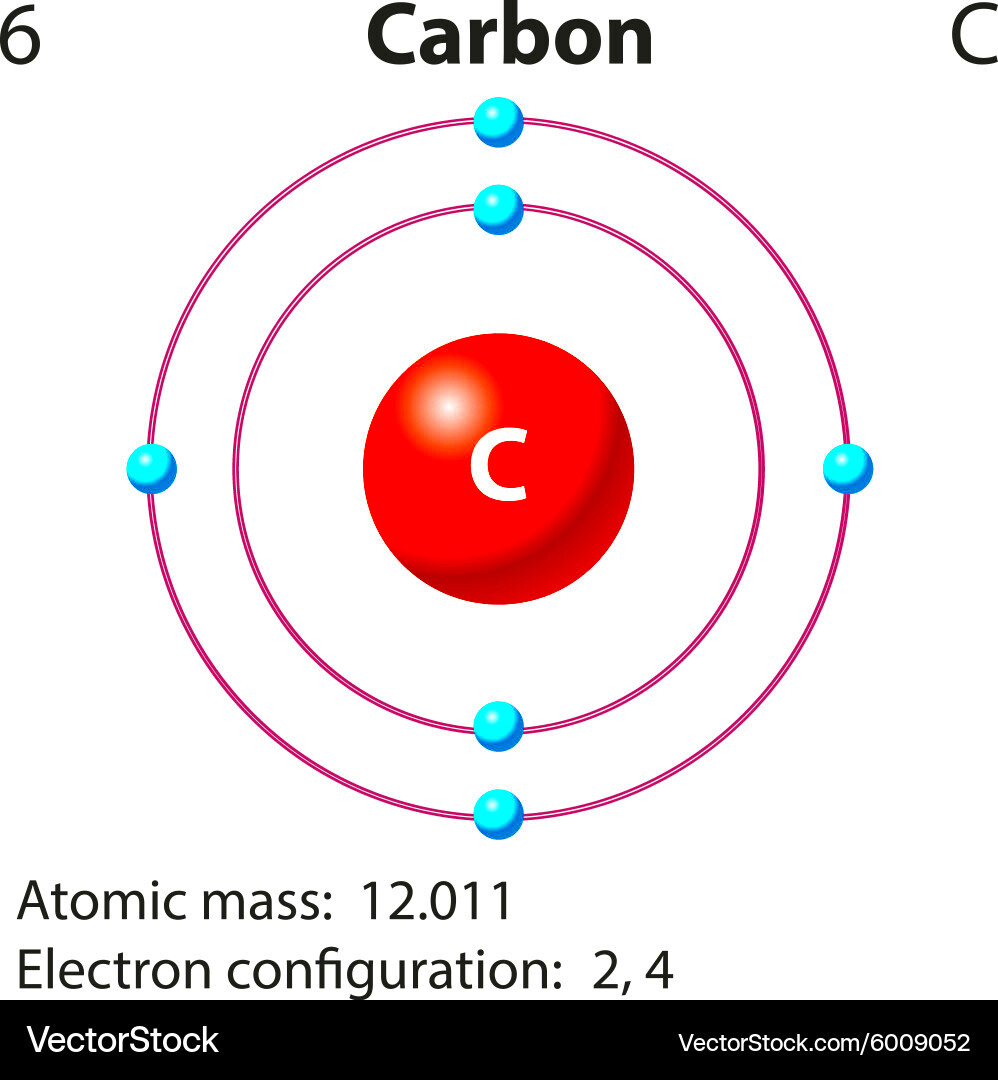
In the digital age, there are numerous tools and software that scientists and educators use to visualize carbon atoms and their bonds. These tools help create accurate, interactive models that improve understanding and learning. Some popular tools include:
| Tool/Software | Features |
|---|---|
| Avogadro | Avogadro is a free, open-source tool that allows users to create and manipulate 3D molecular structures, making it perfect for visualizing carbon atoms in various molecules. |
| ChemDraw | A popular tool in chemical research, ChemDraw allows users to create detailed 2D and 3D molecular diagrams and is often used for carbon atom representations in academic papers. |
| RasMol | This software specializes in molecular visualization, offering users the ability to view complex 3D models, including carbon atoms in protein structures. |
| Jmol | Jmol is an open-source Java viewer that supports 3D molecular visualization, including interactive carbon atom models, ideal for online presentations and educational materials. |
These tools provide a variety of ways to represent carbon atoms, from simple static images to interactive 3D models. They help students, researchers, and educators to better understand atomic structures and molecular behavior.
Also Read This: A Quick Guide to Downloading Alamy Photos in the US
Benefits of Visualizing Carbon Atoms in Educational Content
Visualizing carbon atoms in educational content offers several benefits, especially when teaching complex scientific concepts. By turning abstract ideas into tangible images, students and professionals alike can better understand the critical role carbon plays in chemistry and biology. Here’s how visualizing carbon atoms improves learning:
- Improved Understanding: Visual aids make complex information easier to grasp. By seeing how atoms interact, learners can better understand chemical reactions, molecular shapes, and bond formation.
- Engagement: Interactive models and clear visuals make the learning process more engaging. When students can manipulate 3D models of carbon atoms, they feel more involved in the subject matter.
- Enhanced Memory Retention: Studies show that learners retain information better when they see it. Visualizing carbon atoms in various structures helps solidify understanding and improve long-term memory.
- Hands-On Learning: Software tools that allow students to create or modify molecular models offer a hands-on approach to learning. This interactive experience strengthens their understanding of chemistry.
These benefits are especially important in fields like chemistry and biology, where understanding atomic structures and molecular interactions is key. Visualizing carbon atoms not only makes learning more enjoyable but also deepens understanding and encourages critical thinking in scientific study.
Also Read This: Joining Alamy: A Beginner’s Guide to Signing Up and Getting Started
Common Challenges in Creating Carbon Atom Representations
While representing carbon atoms in various forms of media is crucial for understanding molecular structures, it comes with its own set of challenges. Whether using physical models or digital tools, accurately representing carbon atoms can be complex. Some of the common difficulties include:
- Accuracy of Bond Angles: Carbon atoms form four bonds, but the angles between them can vary depending on the type of bond and the molecule. Achieving perfect representation of bond angles, especially in 3D models, can be tricky.
- Model Simplifications: Many visualizations simplify atomic structures, but this can lead to a loss of detail. For example, in space-filling models, atoms may overlap, making it harder to understand how they truly interact.
- Visual Complexity: As molecules grow larger, visualizing the interactions of carbon atoms within the larger structure becomes more challenging. Large molecules can look cluttered or overly complicated when depicted in traditional models.
- Software Limitations: Some software may not have the capability to fully represent carbon atoms in every situation. Complex molecular shapes or intricate bonding patterns can be difficult to create and visualize accurately using standard tools.
- Scale of Representation: The scale of carbon atoms can sometimes be problematic. Representing a single carbon atom and how it interacts with others at the same scale can be difficult, especially when illustrating larger or smaller molecules.
Despite these challenges, advancements in both physical modeling techniques and software tools have made it easier to represent carbon atoms more accurately. The key is balancing simplicity for clarity with detail for precision.
Also Read This: Is Getty Images Images Safe? Ensuring Trust and Legitimacy in Your Stock Photography
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions related to carbon atom representations:
- What is the most accurate way to represent carbon atoms?
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, 3D molecular models and space-filling models are often the most accurate for depicting carbon atoms and their interactions in a way that is easy to understand. - Why do carbon atoms form four bonds?
Carbon atoms have four electrons in their outer shell, which allows them to form four bonds with other atoms to achieve stability, following the octet rule of chemistry. - What are some free tools for visualizing carbon atoms?
Free tools like Avogadro, Jmol, and RasMol are popular for visualizing carbon atoms and molecules. These tools allow users to create detailed models and interact with them in 3D. - Why is it important to represent carbon atoms in education?
Representing carbon atoms visually helps students and professionals better understand molecular structures, chemical reactions, and how carbon contributes to the diversity of organic compounds. - How do different models of carbon atoms differ?
The ball-and-stick model shows the geometry of molecules, while the space-filling model shows the actual size and spatial relationship of atoms. Both have their strengths depending on the context.
Conclusion
In conclusion, representing carbon atoms visually is an essential aspect of understanding the building blocks of life and molecular science. Whether you're a student, teacher, or scientist, these visualizations help simplify complex concepts and make learning more accessible. While challenges remain in creating accurate representations, advancements in technology and software tools have made it easier than ever to create detailed and interactive models of carbon atoms. By using various methods like ball-and-stick models, space-filling models, and 3D software, we can gain a deeper understanding of how carbon atoms interact and form the foundation of organic chemistry.
As our understanding of carbon's role in the molecular world continues to evolve, so too will the ways we represent these vital atoms. Whether you're teaching a class or studying for an exam, mastering the visual representation of carbon atoms will enrich your knowledge and help you make connections that are vital in the scientific world.
 admin
admin








