The Zimmermann Telegram was a pivotal moment in history, acting as a catalyst that drew the United States into World War I. Sent in January 1917, this secret communication from German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann to Mexico proposed a military alliance against the U.S. As tensions were rising, this bold move not only shocked American leaders but also ignited a wave of nationalist sentiment among the American public. Let’s dive deeper into the details of this intriguing telegram and its implications.
The Context of World War I

To truly appreciate the Zimmermann Telegram, we need to understand the broader context of World War I. The war began in 1914, primarily involving European powers. Here’s a quick overview of the key players:
- Allied Powers: France, the United Kingdom, Russia, and later the United States
- Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria
Initially, the United States maintained a position of neutrality, influenced by a mix of isolationist sentiments and economic ties to both sides. However, several factors began to shift public and political opinion:
- Unrestricted Submarine Warfare: Germany’s policy of attacking ships, including civilian vessels, raised alarm. The sinking of the Lusitania in 1915, which killed 128 Americans, was a significant turning point.
- Economic Interests: American banks and businesses had strong financial ties to the Allies and stood to lose much if they were defeated. Loans to Britain and France increased, further entwining U.S. interests in the conflict.
- Propaganda and Public Opinion: Stories of German atrocities circulated widely, swaying public sentiment against the Central Powers. Newspapers played a crucial role in shaping these perceptions.
As 1917 approached, tensions escalated. The German government announced its intention to resume unrestricted submarine warfare, a decision that threatened American lives and commerce. It was against this backdrop that the Zimmermann Telegram emerged, exacerbating an already tense situation.
The telegram itself suggested that if the U.S. entered the war, Mexico should attack the U.S. and, in return, Germany would support Mexico in reclaiming lost territories: Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. This proposal was not only audacious but also showed Germany's desperation as the war dragged on.
When the British intercepted and decoded the telegram, they shared it with the U.S. government, which caused an immediate stir. The American public was outraged, and President Woodrow Wilson, who had been advocating for peace, found it increasingly difficult to maintain neutrality. The telegram acted as a lit match to the already simmering tensions between the U.S. and Germany, leading to a significant shift in U.S. foreign policy.
In summary, the Zimmermann Telegram was not just a piece of diplomatic correspondence; it was a reflection of the complex interplay of warfare, nationalism, and international relations during a tumultuous period in history. Understanding its context helps us grasp why it had such a profound impact on the United States and the world at large.
Also Read This: How to Use Multiple Telegram Accounts on One Device
3. Key Players Involved in the Telegram
To fully grasp the significance of the Zimmermann Telegram, it's essential to understand the key players involved in this pivotal moment in history. The telegram was a product of various individuals and diplomatic tensions, each contributing to its dramatic impact on the United States' entry into World War I.
Arthur Zimmermann, the German Foreign Minister, was the mastermind behind the telegram. His plan aimed to entice Mexico into joining the war on the side of the Central Powers. Zimmermann believed that if Mexico could secure a victory against the United States, it would regain territories lost during the Mexican-American War, namely Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. This ambitious plan reflected Germany's desperation as they faced increasing pressure from Allied forces.
Walther von Eckardt, the German Ambassador to Mexico, played a crucial role as well. He was the one receiving the telegram and facilitating communication with Mexican officials. Eckardt's task was to ensure that the message reached the right people in the Mexican government and to persuade them to consider Germany's offer seriously.
On the Mexican side, the primary figure was Venustiano Carranza, the President of Mexico at the time. Carranza's government was in a delicate position. Although they were experiencing internal turmoil due to the Mexican Revolution, Carranza had to weigh the potential benefits of aligning with Germany against the risks of provoking the United States. His decision-making would ultimately influence Mexico's response to the telegram.
Additionally, there were indirect players like President Woodrow Wilson and his administration. Wilson was deeply committed to maintaining U.S. neutrality in the war. However, the telegram's interception and its contents sparked a significant shift in public opinion and government policy. Wilson's response to the telegram was pivotal in rallying the nation towards war.
Thus, the Zimmermann Telegram was not just a simple message; it involved a network of influential individuals, each with their own agendas and motivations. This complex interplay ultimately led to a tipping point in American history.
Also Read This: How to Get Verified on Telegram for Enhanced Features
4. What the Zimmermann Telegram Contained
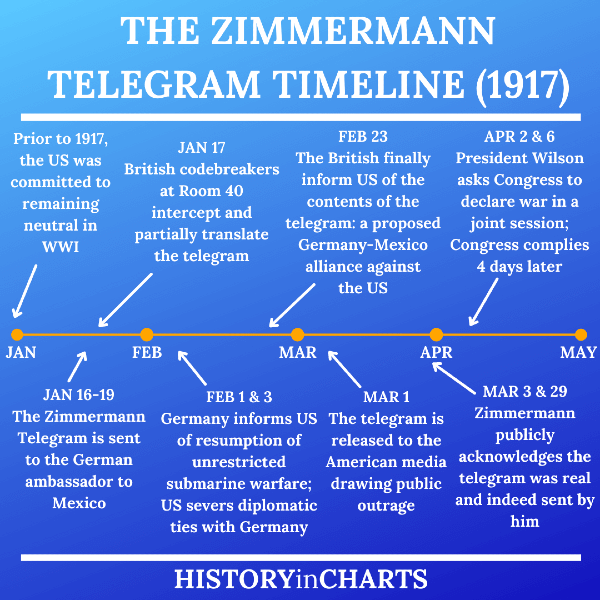
The Zimmermann Telegram was more than a mere communication; it was a bold diplomatic maneuver that altered the course of history. Sent on January 16, 1917, the telegram contained several critical elements that would shock the United States and fuel its entry into World War I.
Here’s a breakdown of the main points contained in the telegram:
- Alliances and Military Support: The telegram proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico. In exchange for Mexico’s support against the United States, Germany promised to assist in recovering lost territories: Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona.
- Support for Japan: Germany also suggested that Mexico reach out to Japan to join the alliance. This broader strategy aimed to create a united front against the United States, further complicating the geopolitical landscape.
- Encouragement of Hostilities: The message encouraged Mexico to take immediate military action against the U.S., which highlighted Germany's desperation as they sought to divert American resources and attention away from Europe.
- Secrecy and Urgency: The telegram emphasized the need for secrecy and quick action, reflecting the urgency of Germany’s situation in the ongoing war.
When British intelligence intercepted the telegram and decoded it, they recognized its potential to change the tide of public sentiment in the United States. The British shared this explosive information with the U.S. government, leading to outrage among the American populace.
In summary, the Zimmermann Telegram was a strategic gambit by Germany that ultimately backfired, galvanizing the American public and government to rally against the Central Powers. Its contents not only showcased Germany’s desperation but also illuminated the intricate web of international diplomacy during World War I.
Also Read This: How to Get Unbanned from Telegram
5. The United States' Reaction to the Telegram
The Zimmermann Telegram, sent in January 1917, was like a spark in a powder keg of international tension. When the British decrypted it and shared it with the United States, the reaction was immediate and intense. Many Americans were shocked and outraged by Germany's proposal to Mexico to reclaim territories lost during the Mexican-American War, specifically Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. This was not just a diplomatic message; it was perceived as a direct threat to U.S. sovereignty.
In the days following the telegram's revelation, public opinion began to shift dramatically. Prior to this, many Americans had been ambivalent about entering World War I. But the telegram changed the narrative. The idea that Germany was attempting to incite Mexico against the U.S. stirred feelings of nationalism and anger. Major newspapers of the time, like the New York Times and the Chicago Tribune, seized on the story and fueled the flames of public sentiment.
- Media Coverage: Newspapers published sensational headlines, such as "Germany's Plot to Set Mexico on Fire," which painted the telegram as a clear act of aggression.
- Public Demonstrations: Across the country, rallies and protests erupted, calling for action against Germany.
- Government Response: President Woodrow Wilson, who had campaigned on the promise of keeping the U.S. out of the war, found himself in a politically precarious situation.
By March 1917, the pressure was mounting. Wilson requested that Congress declare war on Germany, citing the telegram as a pivotal reason. In his speech, he emphasized that “the world must be made safe for democracy,” framing the war as a moral imperative. On April 6, 1917, Congress officially declared war, marking a significant turning point in U.S. history.
Also Read This: How to Install Telegram on Your Device: Getting Started with Telegram
6. The Political Implications for the U.S.
The political implications of the Zimmermann Telegram were profound and far-reaching. It not only shaped the immediate response to World War I but also influenced U.S. foreign policy for decades to come. Here are some key areas where the impact was particularly significant:
- Shift in Foreign Policy: The telegram catalyzed a shift from isolationism to a more interventionist foreign policy. The U.S. began to see itself as a global leader, willing to engage in international conflicts to protect its interests.
- Strengthening Alliances: The U.S. solidified its relationships with allies such as Britain and France. Cooperation in the war effort laid the groundwork for future alliances, including the formation of the League of Nations.
- Domestic Politics: The war effort united a fractured political landscape. Democrats and Republicans rallied together in support of the war, though tensions would later resurface over issues like the Treaty of Versailles.
- Public Sentiment: The telegram fueled a wave of patriotism that impacted social dynamics within the U.S. It led to increased scrutiny of dissenters and heightened nationalistic fervor, affecting everything from civil liberties to cultural expressions.
In summary, the Zimmermann Telegram was not just a pivotal moment in World War I; it reshaped the trajectory of U.S. politics and foreign relations. The aftermath saw the country emerge from its isolationist stance, paving the way for a more active role on the world stage. As we reflect on this historical event, it’s clear that the ramifications of that single communication extended far beyond the immediate conflict, influencing the course of American history in profound ways.
Also Read This: Does Telegram Tell Others If You Screenshot Their Chat?
7. How the Telegram Changed Public Opinion
The Zimmermann Telegram was a turning point, not just in diplomatic relations but also in how the American public perceived the war in Europe. Prior to the telegram's revelation, many Americans were divided on the issue of entering World War I. Some viewed it as a distant conflict, while others felt a growing sense of connection to the Allies, particularly due to shared cultural ties with Britain and France.
When the contents of the telegram were made public, it sparked outrage across the nation. The idea that Germany was attempting to incite Mexico against the United States was not just a diplomatic affront; it felt like a direct threat to American sovereignty. Bold headlines in newspapers proclaimed the news, and many Americans were left feeling a mixture of fear and anger.
- Nationalism: The telegram ignited a surge of nationalism. Many citizens began to see the war as not just a European conflict, but as something that directly threatened their homeland.
- Media Influence: Newspapers played a crucial role in shaping public opinion. Outlets like the New York Times and the Chicago Tribune ran sensational stories that stoked fears of German aggression, further rallying support for the war.
- Mobilization of Support: Organizations began to form in support of the war effort, including the National Security League, which aimed to prepare the nation for potential conflict.
As a result, the telegram catalyzed a wave of enlistments in the military. Young men rushed to join the ranks to defend their country. The notion that American lives could be at stake due to foreign intrigue galvanized a previously hesitant populace. No longer was the war an abstract issue; it became a matter of national pride and security.
Moreover, the telegram also polarized opinions on neutrality. Those who were previously against U.S. involvement began reconsidering their stance, feeling the need to protect American interests. This shift was evident in town halls, rallies, and discussions across the country. It united many people under a common cause, leading to a surge in pro-war sentiment that would only grow stronger in the months that followed.
8. The Aftermath and Entry of the U.S. into World War I
Following the revelation of the Zimmermann Telegram, the United States found itself at a crossroads. The telegram wasn't just an isolated event; it was a catalyst that propelled the nation towards war. By April 1917, just a few months after the telegram's disclosure, President Woodrow Wilson asked Congress to declare war on Germany. This was a dramatic shift from his earlier position of neutrality.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| January 16, 1917 | Zimmermann Telegram sent to Mexico |
| February 1917 | Telegram intercepted and decoded by British intelligence |
| March 1, 1917 | First public revelation of the telegram |
| April 6, 1917 | U.S. declares war on Germany |
This decision marked a significant shift in American foreign policy. No longer could the U.S. afford to remain on the sidelines while its interests and citizens were threatened. The entry into the war was met with a mix of celebration and trepidation. Many viewed it as necessary for ensuring the safety and stability of the nation.
The aftermath of the telegram also saw the U.S. ramping up its military preparedness. The Selective Service Act was passed, leading to a draft that brought millions of young men into military service. The country mobilized resources as industries shifted to wartime production—everything from munitions to food supplies.
In the end, the Zimmermann Telegram exemplified how a single piece of communication could alter the course of history. It not only changed public opinion but also solidified the United States’ role on the world stage as a significant military power. By the time the war concluded in 1918, the U.S. had emerged as a crucial player, reshaping global dynamics for decades to come.
 admin
admin








