When it comes to images, there's always a balancing act between quality and file size. High-quality images often have larger file sizes, while smaller files typically lose some visual clarity. For web use, especially, it's essential to find the sweet spot: keeping images looking good without making the file too large. After all, larger files take up more storage space and can slow down web page loading times.
In this post, we'll explore how to reduce image file size without compromising too much on quality. We’ll cover different techniques and tools that can help you optimize your images for the web or storage needs.
Why Reducing File Size Matters
Reducing image file size is essential for several reasons. Whether you're managing a website, working on a design project, or simply organizing your photos, smaller file sizes bring multiple benefits:
- Improved website performance: Smaller images load faster, resulting in a smoother user experience and quicker page load times, which are crucial for SEO and retaining visitors.
- Reduced bandwidth usage: When you reduce the file size of an image, you use less data. This is especially important for mobile users or websites with limited bandwidth.
- Better storage management: Small file sizes help keep your storage efficient and prevent running out of space quickly. This is helpful for both personal use and large-scale digital projects.
- Cost-effective: For businesses or developers, reduced file sizes can lower hosting costs by requiring less storage and bandwidth.
By reducing image file sizes, you're setting yourself up for faster, more efficient digital experiences without sacrificing too much on image quality.
Common Methods for Image File Size Reduction
There are several ways to reduce the file size of images. Here are the most common methods, each serving a different purpose depending on your specific needs:
| Method | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | Compression reduces file size by removing some of the image data. There are two main types: lossy (which reduces quality to a greater degree) and lossless (which preserves quality). | Web images, social media, and e-commerce platforms. |
| Resizing | Resizing simply involves changing the dimensions of the image. Smaller dimensions equal smaller file size, but too much reduction can lead to quality loss. | Images that are too large for display or print. |
| Changing File Format | Choosing a more efficient file format can significantly reduce file size. For example, JPEG is good for photos, while PNG is better for images with transparency. | Images with clear details and transparent backgrounds. |
| Cropping | Simply cutting out unneeded parts of the image reduces both size and file complexity. | Images with unnecessary space or background. |
Each of these methods can be used alone or combined depending on the specific requirements of your image. For example, resizing an image and then applying compression can lead to significant file size reduction without a dramatic drop in quality.
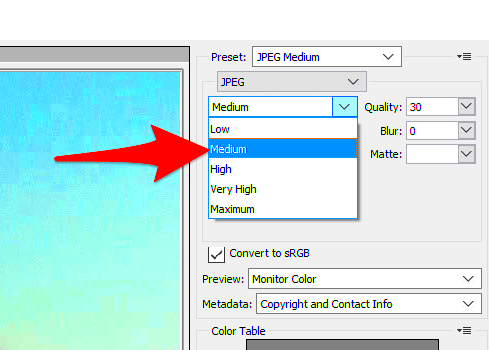
Using Compression to Lower Image File Size
Compression is one of the most effective ways to reduce an image's file size. It works by removing some of the image's data, making the file smaller. There are two primary types of compression: lossless and lossy. Understanding the difference between these can help you choose the best approach for your images.
Lossy compression reduces file size by removing some image data that the human eye may not notice. While it does decrease the image's quality slightly, the difference is often unnoticeable unless the compression level is too high. This method is great for photos and web images, where file size reduction is more important than perfect quality.
Lossless compression, on the other hand, compresses images without losing any quality. It works by reducing redundant data, making the file smaller while preserving every detail of the image. Lossless compression is ideal for images that need to retain fine details, like logos or graphics.
Some popular tools for image compression include:
- JPEGmini – A great tool for compressing JPEG files without sacrificing much quality.
- ImageOptim – A tool for Mac users that supports both lossless and lossy compression.
- TinyPNG – An online tool for compressing PNG and JPEG files with excellent results.
Compression is an essential tool in your image optimization toolkit, offering an easy way to significantly reduce file sizes while maintaining the best possible quality for your needs.
Resizing Images to Reduce File Size
Resizing is another simple and effective way to reduce image file sizes. When you resize an image, you're essentially changing its dimensions—either reducing or increasing its width and height. Smaller dimensions typically lead to smaller file sizes. However, it's important to find the right balance between size and quality.
If you have a large image that you don’t need at full resolution, resizing it can dramatically reduce its file size without compromising too much on visual appeal. For example, if you're creating an image for a website, you don't need the high resolution required for printing. A smaller image will still look sharp on most screens but will load much faster.
Here are some key points to keep in mind when resizing images:
- Consider the end use: For web use, resize images to the specific dimensions required for the page.
- Maintain aspect ratio: Always maintain the image’s aspect ratio when resizing to avoid distortion.
- Choose the right resolution: For digital images, 72 DPI (dots per inch) is typically enough, whereas for print images, you'll need at least 300 DPI.
You can resize images using tools like Photoshop, GIMP, or even online image resizers. The key is to experiment with different sizes to see how much you can reduce the file while keeping the image looking good.
Choosing the Right Image Format
The file format you choose for your image plays a significant role in determining its file size and quality. Different formats offer various trade-offs between quality and compression. Choosing the right one depends on the type of image you're working with and how you intend to use it.
Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used image formats:
| Format | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photographs and complex images | High compression, small file sizes, great for photos | Lossy compression, can lose quality with high compression |
| PNG | Images with transparency, logos | Lossless compression, supports transparent backgrounds | Larger file sizes compared to JPEG |
| GIF | Simple graphics, animations | Supports animation, lossless compression | Limited to 25 |