Importing data from images into Google Sheets can save you a lot of time, especially when you need to quickly process large amounts of information. Instead of manually entering the data, you can use technology to extract the text or numbers directly from the image and import them into your spreadsheet. This is especially useful for receipts, invoices, forms, and even printed documents that contain structured data. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in importing data from images into Google Sheets and how you can make the process easier and more efficient.
Why You Might Need to Import Data from Images
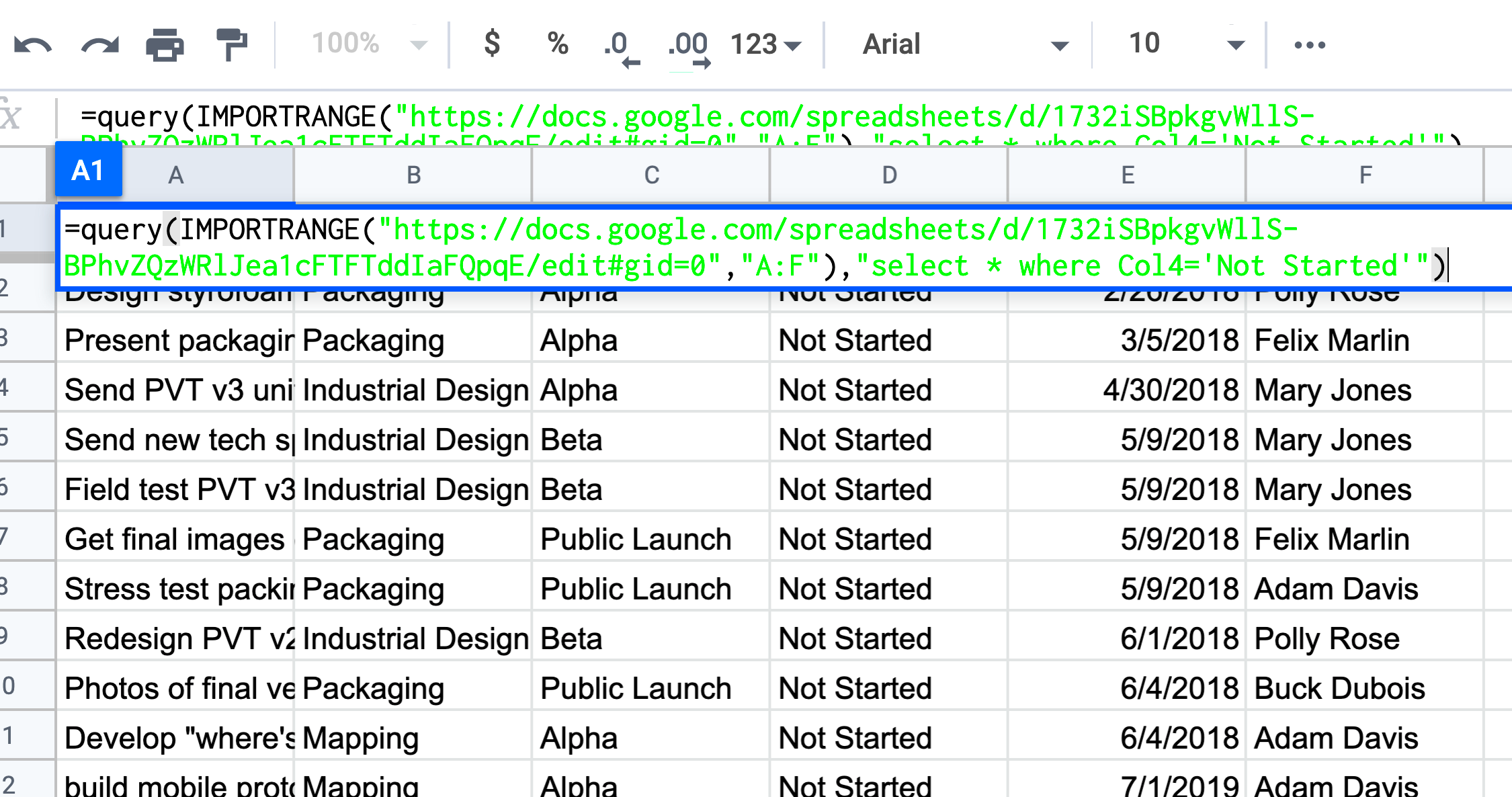
There are several reasons why you may want to import data from images into Google Sheets:
- Speed and Efficiency: Manually entering data from images is time-consuming. Importing data directly saves time and effort.
- Accuracy: Optical character recognition (OCR) tools can help eliminate human errors that occur during data entry.
- Convenience: Many documents, such as invoices or receipts, are in image formats. Using OCR, you can easily extract the information and organize it in a Google Sheet for better accessibility and management.
- Cost-effective: Automating data extraction is cost-effective for businesses that need to process large volumes of data regularly.
By importing data from images, you can streamline workflows and ensure that data is organized properly, making it easier to analyze or share with others.
Also Read This: How to Record Songs from YouTube
How to Prepare Your Image for Data Extraction
Before you can extract data from an image, there are a few key steps you need to take to ensure that the process goes smoothly:
- Ensure Image Quality: The better the quality of the image, the more accurate the data extraction will be. Clear, high-resolution images are essential for OCR tools to recognize text properly.
- Correct Orientation: Make sure that the image is properly oriented. Text should be upright, and there should be minimal distortion.
- Use Clean, Simple Backgrounds: Text that contrasts clearly with the background (like black text on a white background) is easier for OCR tools to detect. Avoid cluttered or overly busy images.
- Focus on Text: If possible, crop the image to focus only on the area containing the text you need to extract. This helps prevent the OCR tool from picking up irrelevant information.
- Ensure Legible Fonts: OCR tools work best with standard fonts. If the image contains handwritten text or fancy fonts, the extraction process may not be as accurate.
Taking these simple steps before uploading the image can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of data extraction into Google Sheets.
Also Read This: Sonic Sorcery: Enhancing Spotify with Moises – A How-To Guide
Using Google Sheets' Built-in Tools to Import Data
Google Sheets offers some handy built-in tools that can help you import data from images, especially using its integration with Google Drive and Google Docs. The OCR (Optical Character Recognition) feature within Google Docs can automatically detect and extract text from images and convert it into editable format. This text can then be transferred to Google Sheets for further analysis or processing. Here's how you can make the most of these tools:
- Upload the Image to Google Drive: First, upload your image to Google Drive by dragging and dropping the file into the drive or using the "New" button.
- Open Image with Google Docs: Once the image is uploaded, right-click the image file and select “Open with” and then choose “Google Docs.” Google Docs will use its OCR capabilities to extract the text from the image and open it in a new document.
- Copy and Paste into Google Sheets: Once the text is extracted in Google Docs, simply copy it and paste it into a Google Sheet where you can organize or analyze the data further.
This method is straightforward and doesn’t require any additional software or complex setup. However, keep in mind that the OCR feature may not work perfectly for all images, especially if the text quality is poor.
Also Read This: How to Convert Dailymotion Videos to MP3 Files – A Complete Tutorial
How to Use Google Vision API for Data Extraction
For more advanced image data extraction, you can use the Google Vision API. This tool allows you to analyze images with high precision, extracting not only text but also other elements like objects, logos, and landmarks. Here’s how you can use the Vision API to extract data from images:
- Set Up the Google Cloud Account: First, you need a Google Cloud account. Sign up and enable the Vision API by creating a project in the Google Cloud Console.
- Upload Your Image: Once the API is set up, you can upload your image to Google Cloud Storage or use the API to directly analyze the image from a URL.
- Request Text Extraction: Use the Vision API to request text extraction. The API will return a JSON response containing all the detected text, along with its position in the image.
- Format the Data: After retrieving the extracted text, you can clean it up and format it into a structure that fits your Google Sheets. This could involve using programming languages like Python or JavaScript for data processing.
The Google Vision API is a powerful tool, especially for complex images, but it does require some technical know-how. You can also integrate it into custom applications for automatic data extraction workflows.
Also Read This: Fixing Grainy Images for Clearer Quality
Manual Methods for Transferring Data from Images
Although automated tools like OCR and APIs can help speed up data extraction, there are times when you might need to do things manually. If the image quality is poor or the text extraction tools don't give you the results you need, here are some manual methods for transferring data:
- Re-type the Data: The simplest method, though time-consuming, is to manually type the data from the image into Google Sheets. This method ensures the highest accuracy if you're dealing with a small amount of data.
- Use Image Editing Tools: Sometimes, enhancing the image using editing software like Photoshop or GIMP can help make the text more legible. After editing, you can use OCR tools again for better results.
- Voice-to-Text Input: If the data in the image is readable but still too tedious to type, consider using voice recognition software to dictate the data into Google Sheets.
Manual methods can be useful, especially when you only have a few data points to transfer. However, they are not as efficient as automated tools for large datasets.
Also Read This: Is Dailymotion Similar to YouTube? A Comparison of Two Video Platforms
Common Issues You Might Face and How to Solve Them
When importing data from images to Google Sheets, you might face a few challenges along the way. These issues can stem from various factors such as poor image quality, complex layouts, or even the limitations of the tools you’re using. Here are some common problems and how to solve them:
- Poor Image Quality: If the image is blurry or low-resolution, the OCR tool may struggle to extract text accurately. To solve this, make sure your images are clear, high-resolution, and well-lit. Using photo editing tools to sharpen the image before uploading can also help.
- Incorrect Text Extraction: OCR tools may misinterpret text, especially if it's in a non-standard font or handwriting. If the extracted data contains errors, consider manually editing it in Google Sheets. Alternatively, improve the image quality or use a more advanced tool like the Google Vision API for better accuracy.
- Formatting Issues: When copying data from Google Docs to Google Sheets, you may encounter formatting problems such as misplaced text or inconsistent spacing. To resolve this, you can use the "Find and Replace" tool in Google Sheets to correct formatting quickly, or manually adjust columns and rows.
- Limited OCR Tool Features: The built-in OCR in Google Docs has its limitations, especially with complex data. If the data extraction process doesn’t meet your expectations, using more advanced APIs like Google Vision can provide better results.
By understanding and addressing these common challenges, you can make the process of importing data from images much smoother and more effective.
Also Read This: How to Cite an iStock Image in APA Format
Conclusion
Importing data from images to Google Sheets is an efficient way to manage and analyze information from various sources. Whether you use Google Sheets' built-in OCR tool, the more advanced Google Vision API, or manual methods, there are plenty of ways to make the process work for you. While challenges like poor image quality or incorrect text extraction may arise, most issues can be solved with simple fixes, such as enhancing the image or using a different tool. By following the tips outlined in this guide, you'll be able to streamline your data entry tasks and save valuable time.
FAQ
1. Can I use Google Sheets’ built-in OCR tool on any type of image?
Google Sheets’ built-in OCR tool works best on images with clear, legible text. It may struggle with handwritten text or very poor-quality images. For better results, ensure that the text is well-lit and high-resolution.
2. Is the Google Vision API free to use?
The Google Vision API offers limited free usage per month. After that, charges apply based on the number of images processed. You can check Google Cloud’s pricing details to see if it fits your needs.
3. Can I extract data from images with complex layouts?
For complex layouts, OCR tools might have trouble correctly identifying the text. In such cases, using advanced tools like the Google Vision API or manually cleaning up the extracted data is a better option.
4. How can I fix errors in the extracted text?
If the OCR tool misinterprets the text, you can manually correct it in Google Sheets or use the "Find and Replace" feature to fix common mistakes quickly. Improving image quality can also help prevent errors in the first place.
5. What’s the best way to handle data extraction for handwritten text?
Handwritten text is more difficult to extract accurately. You may need to use specialized software or manually transcribe the information. Alternatively, try improving the image quality to help OCR tools better recognize the text.
 admin
admin








