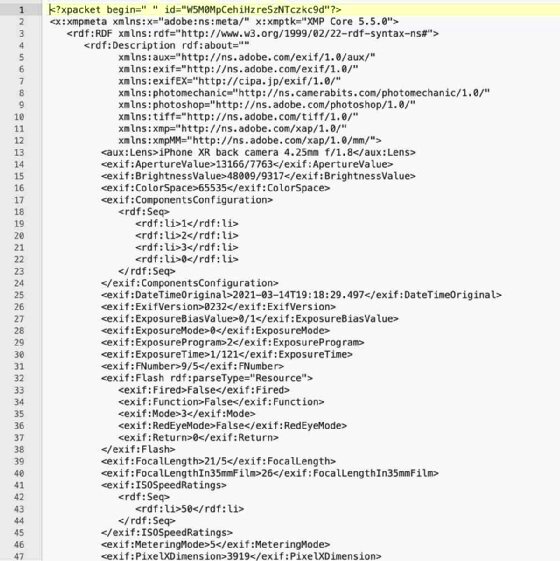
Image metadata might sound like a technical term, but it simply refers to the hidden data embedded within an image file. This data can provide you with detailed information about the
Why Image Metadata Is Important
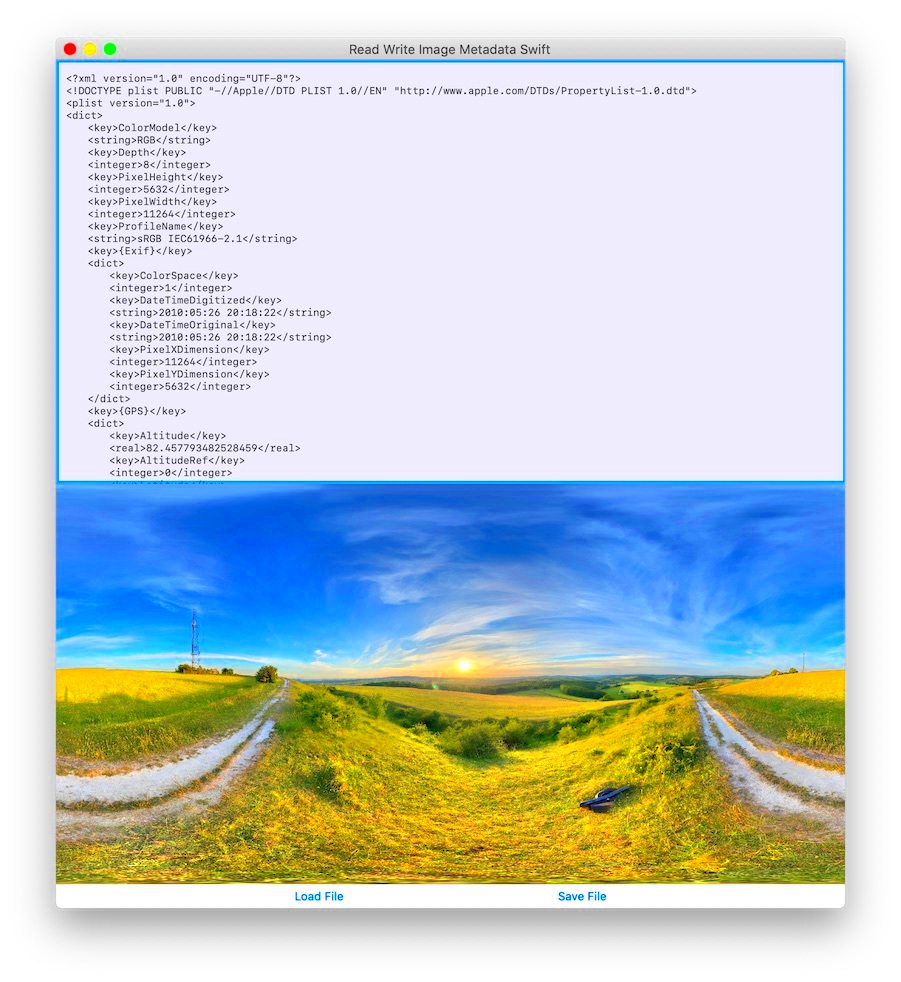
Image metadata serves more than just an informational purpose; it plays a critical role in various areas like copyright tracking, authenticity verification, and usage rights management. For example:
- Copyright Protection: Metadata can contain copyright information, which helps protect the image owner’s intellectual property.
- Image Authenticity: Metadata can reveal when and where an image was taken, providing proof of its authenticity.
- Search Engine Optimization: Metadata can help images rank better in search engines by including keywords and descriptions.
- Tracking Image Usage: It enables you to trace where and how an image has been used across the internet.
Without proper metadata, an image could lose its attribution, making it harder to track its origin and misuse it. So, by checking and understanding the metadata, you protect both the image creator and yourself.
Also Read This: How to Download Music from Shutterstock: A Step-by-Step Guide
Types of Metadata Found in Images
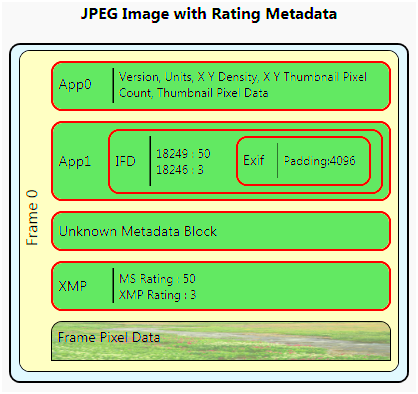
When you open the metadata of an image, you'll often encounter a variety of formats, each offering different types of information. Here are the most common types of metadata you’ll come across:
| Metadata Type | What It Includes |
|---|---|
| EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) | Details about the camera settings like exposure time, focal length, ISO, date and time, and GPS coordinates (if enabled). |
| IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council) | Information about the image’s copyright, author, title, and description. Used primarily for editorial and news content. |
| XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform) | Flexible metadata format that can store a wide range of information, including rights and license details, and keywords for searchability. |
Each type of metadata serves a unique purpose, helping you track everything from technical image settings to ownership and licensing. Knowing what each type reveals can help you understand the full picture of an image's background.
Also Read This: Step-by-step Guide: How to Make a Streamable
How to Access Image Metadata
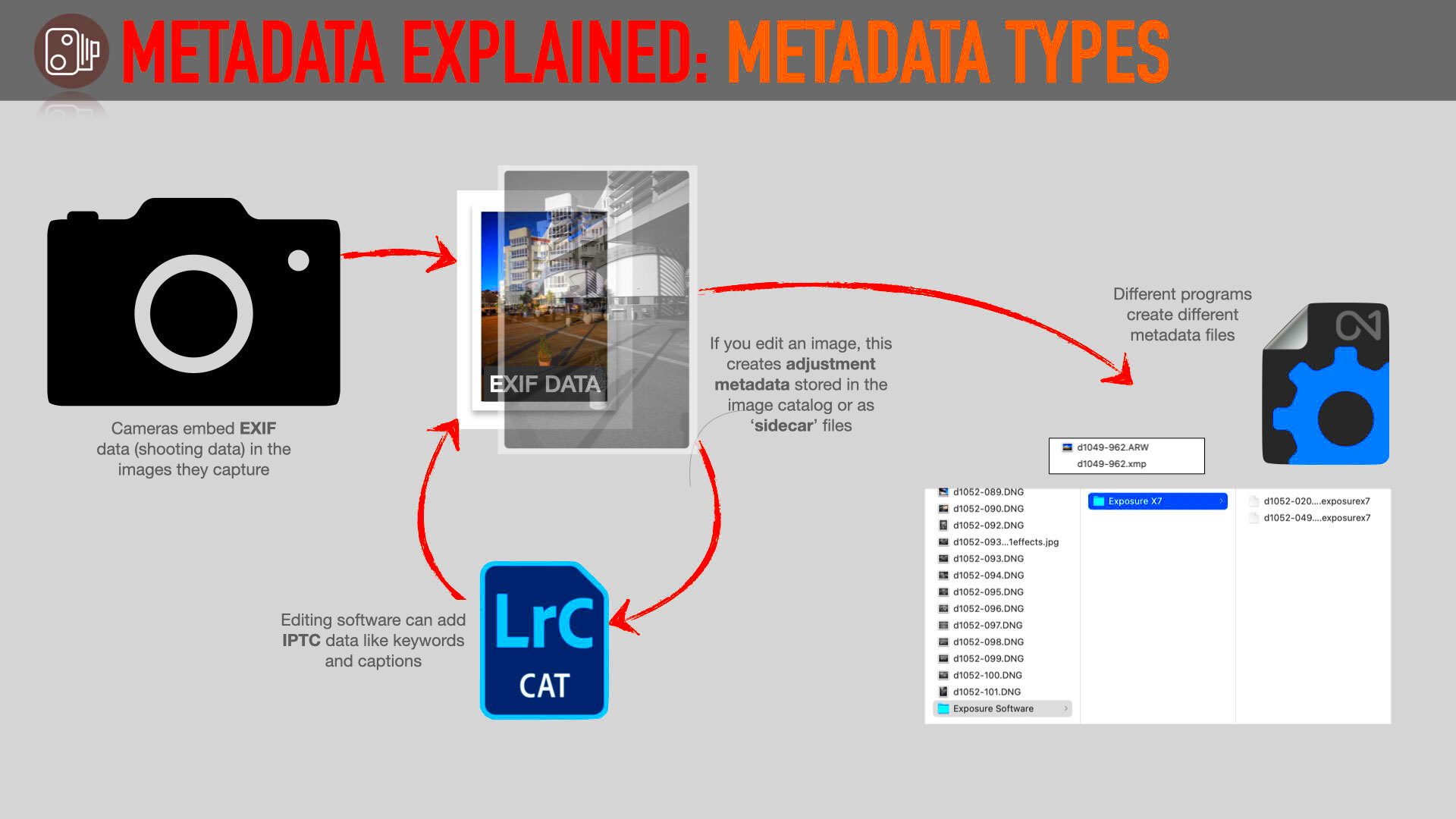
Accessing image metadata is a simple process, but it requires the right tools. Whether you're using a computer or a mobile device, there are several ways to view metadata without needing advanced software. Here are a few methods you can use:
- Using File Properties (Windows): Right-click on the image file, select "Properties," then go to the "Details" tab to view metadata such as camera settings and date taken.
- Using Preview (Mac): Open the image in the Preview app, click "Tools," then select "Show Inspector" and choose the "i" tab to view EXIF and other metadata.
- Using Online Tools: There are many free online metadata viewers where you simply upload an image to extract its metadata. Popular options include websites like metapicz.com or get-metadata.com.
- Using Dedicated Software: Programs like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom allow you to access and edit more detailed metadata, especially for professional photographers.
By using these methods, you can easily access the metadata of any image to learn more about its source, settings, and copyright information. Remember, some metadata may be stripped when images are uploaded to certain platforms, so it's important to check before relying on this data.
Also Read This: How to Combine Images from 123RF for Collage Art
Reading EXIF Data in Images
EXIF data is one of the most common types of image metadata, and it’s typically embedded in the file by the camera or smartphone when the picture is taken. This data can provide a wealth of information about the image, such as:
- Camera Settings: Exposure time, aperture, ISO, focal length, and white balance settings.
- Geolocation: GPS coordinates, if enabled, showing where the photo was taken.
- Date and Time: The exact date and time the image was captured.
- Image Resolution: The image’s dimensions, which can help assess quality and cropping needs.
To read EXIF data, you can use a simple image viewer or photo editing software that supports metadata. If you want to dig deeper into the technical side, EXIF data can also be accessed through specialized programs like ExifTool, which displays all the hidden details. Knowing how to read this data is invaluable, especially for photographers looking to understand the conditions under which their images were taken.
Also Read This: Adobe Stock vs 500px: Choosing the Right Platform for Selling Photos
Understanding IPTC and XMP Metadata
While EXIF data is primarily concerned with technical image information, IPTC and XMP metadata formats focus more on content-related details, such as copyright, authorship, and image description. Here's a breakdown of each format:
| Metadata Type | What It Includes |
|---|---|
| IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council) | IPTC metadata is used mostly in journalism and media. It includes fields for the image’s title, creator, copyright information, and keywords for better searchability. It also contains captions and licensing details. |
| XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform) | XMP is a more flexible and modern format that can handle a wide range of metadata, including rights management, copyright info, image descriptions, and keywords. XMP data can be embedded in the image itself or stored separately. |
These metadata formats help ensure proper attribution and usage rights, making them especially useful for photographers and content creators who need to manage and protect their work. By understanding and utilizing IPTC and XMP data, you can ensure your images are properly credited, track their usage, and maintain full control over your intellectual property.
Also Read This: How to Shoot and Edit High-Quality Product Photos
Common Use Cases for Image Metadata
Image metadata is not just a bunch of technical information—it's a valuable tool used in many industries. By understanding and utilizing metadata, you can enhance the way you manage and interact with images. Here are some common use cases where image metadata plays a key role:
- Photography: Photographers use metadata to keep track of camera settings, exposure details, and other technical aspects that help them replicate specific shots or learn from past ones.
- Copyright and Attribution: Creators can embed copyright information in the metadata to protect their work and ensure they receive proper credit whenever the image is used.
- Digital Asset Management: Large organizations often use metadata to organize and categorize images in their digital libraries. This allows for easier searching and sorting of thousands of files.
- Marketing and SEO: Digital marketers add keywords, descriptions, and location tags to metadata, boosting an image's visibility in search engines and making it more discoverable to the right audience.
- News and Journalism: Journalists use IPTC metadata to add captions, credit photographers, and tag images with keywords, making it easier to manage large volumes of media content.
- Geotagging: GPS coordinates in EXIF metadata allow for location-based tagging, making it easier to find and sort images based on where they were taken.
In all these cases, metadata adds depth and value to an image, making it easier to track, protect, and use effectively in different contexts.
Also Read This: How to Upload Photos to Getty Images to Sell as a Photographer Submission Guide
Challenges of Image Metadata and How to Overcome Them
While image metadata can be incredibly helpful, it’s not always straightforward to work with. Some common challenges include missing, incorrect, or altered data. Here’s how you can overcome these issues:
- Missing Metadata: Sometimes, images come without metadata or have incomplete data. To fix this, you can manually add metadata using tools like Adobe Lightroom or ExifTool. Additionally, if you are dealing with a bulk collection of images, automated tools can save time by adding or correcting metadata.
- Corrupted or Damaged Metadata: Metadata can get corrupted due to file transfer errors or software issues. To avoid this, always back up your images before editing or transferring them. If metadata corruption occurs, there are tools like ExifTool and PhotoME that can help recover or repair the data.
- Metadata Stripped by Social Media: Many platforms strip away metadata when images are uploaded to protect privacy or reduce file size. While you can’t prevent this on every platform, you can retain metadata by hosting your images on your own website or using platforms that preserve metadata.
- Inconsistent Data: Inconsistent or incorrect metadata can confuse both humans and search engines. Ensuring a standardized approach to metadata—such as using specific fields for copyright, creator, and descriptions—can help improve consistency.
By being aware of these challenges and using the right tools, you can maintain clean, accurate metadata for all your images, ensuring you get the most out of them.
Also Read This: Using YouTube Music in Your iMovie Projects
FAQ
1. What is image metadata?
Image metadata is hidden information embedded within an image file. It includes details such as camera settings, copyright info, location, and more.
2. How can I view image metadata?
You can view metadata by right-clicking the image file and checking the "Properties" on Windows or using "Preview" on Mac. Alternatively, online metadata viewers and software like Adobe Photoshop allow you to inspect more detailed data.
3. Why is image metadata important for SEO?
Metadata helps search engines understand an image’s content, making it easier to index and rank in search results. Adding relevant keywords and descriptions in the metadata can increase an image's visibility.
4. Can metadata be deleted or altered?
Yes, metadata can be deleted or altered, either intentionally or accidentally. Many platforms, especially social media, strip metadata when uploading images. To preserve metadata, use tools that allow you to embed or protect it before sharing.
5. How can I add metadata to an image?
You can add metadata using various tools like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, or free software like ExifTool. These programs let you edit or input additional details like copyright, description, and keywords.
6. Is metadata the same across all image formats?
No, different image formats support different types of metadata. For example, EXIF data is common in JPEG images, while PNG files often store metadata in XMP or other formats.
Conclusion
Understanding image metadata is essential for anyone who works with digital images. From photographers to marketers, metadata offers valuable insights into an image's origin, technical settings, and usage rights. Whether you're using metadata for copyright protection, SEO optimization, or image organization, it can enhance how you manage and track images in your workflow. However, challenges like missing or altered metadata can complicate its use, so it’s important to regularly check and maintain the accuracy of your data. By knowing how to access, read, and manage image metadata, you can maximize its benefits and ensure that your images are well-organized and properly credited.