Image cropping is essential when you need to resize or focus on a specific part of an image. Whether you're preparing visuals for social media, a website, or a printed project, cropping ensures your
Maintaining Aspect Ratio While Cropping
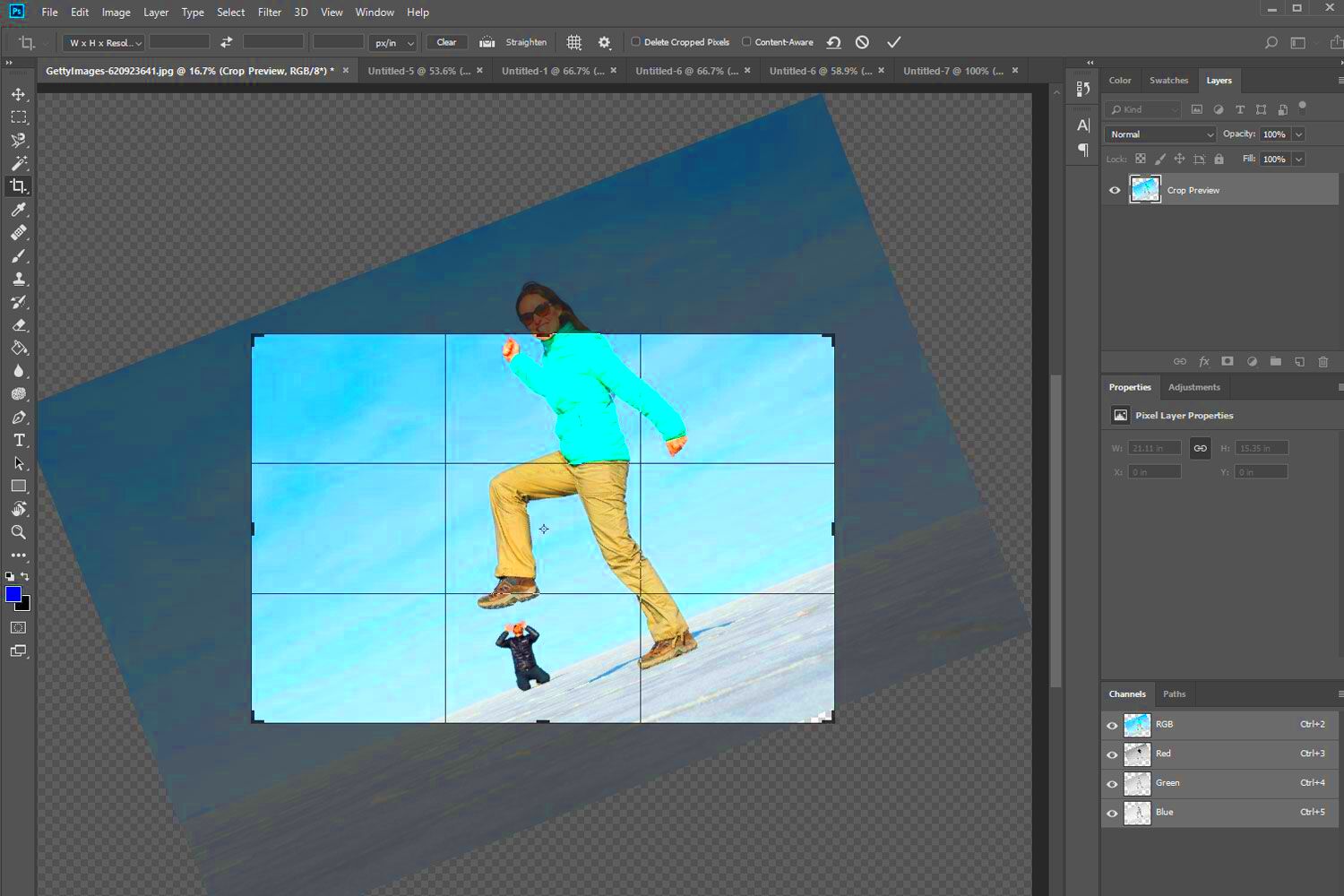
When cropping an image, maintaining the aspect ratio is crucial to avoid distorting the image. The aspect ratio is the relationship between the width and height of the
Here’s how you can keep the aspect ratio intact while cropping:
- Use the “Lock Aspect Ratio” feature: Many image editing tools have an option to lock the aspect ratio, ensuring the proportions stay consistent when cropping.
- Manual aspect ratio input: Tools like Photoshop allow you to set specific aspect ratios like 16:9 or 4:3, which is useful for preparing images for platforms with specific dimension requirements.
- Adjust dimensions proportionally: If you're resizing manually, hold down the Shift key (in most programs) to crop while keeping the original ratio.
Aspect ratio is especially important when you’re creating images for websites, social media, or print. Websites and social platforms often have specific size guidelines. For example, Instagram favors square images (1:1), while widescreen (16:9) works best for YouTube thumbnails.
Also Read This: Editing Adobe Stock Templates in Illustrator
Advanced Cropping Techniques for Creative Results
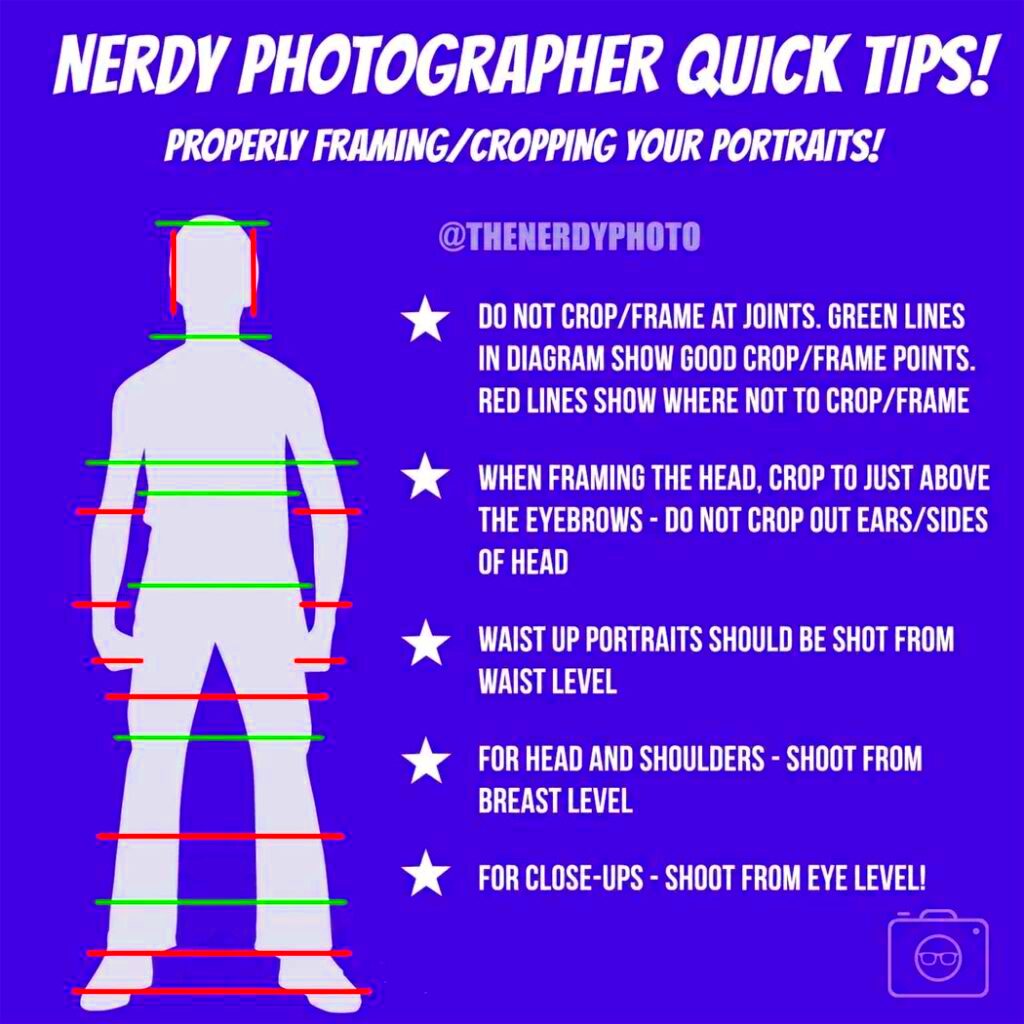
Cropping isn’t just about trimming edges—it can also be used creatively to transform your images. Advanced cropping techniques allow you to focus on specific areas, improve composition, or completely change the mood of a photo. Here are some creative ways to crop your images:
- Rule of Thirds: When cropping, imagine a grid splitting your image into thirds both horizontally and vertically. Place important elements along these lines or at the intersections to create more dynamic and engaging compositions.
- Tight cropping for emphasis: You can crop tightly around your subject to eliminate distractions and bring more focus to the main point of the image.
- Asymmetrical cropping: Cropping off-center can add a sense of movement or drama to an image, making it feel less static and more visually interesting.
- Creative frame cropping: Crop in such a way that it feels like the subject extends beyond the edges of the image. This technique can create an illusion of depth or make the image feel larger than it actually is.
With a bit of experimentation, these techniques can help you use cropping to create powerful visuals that stand out.
Also Read This: Can You Sell Photos on Alamy for Free
Best Practices for Cropping Images for Print
When preparing images for print, cropping is a bit more technical than for digital use. Printed images must maintain high quality and correct proportions to avoid issues like pixelation or uneven borders. Here’s what you should consider when cropping for print:
- Maintain high resolution: Always work with the highest resolution possible to ensure that your cropped image doesn't lose quality. For print, 300 DPI (dots per inch) is the standard.
- Allow bleed margins: If your image will be printed close to the edge of the paper, add extra space (known as bleed) around the edges to avoid white borders. This margin typically ranges from 1/8 to 1/4 inch.
- Check print dimensions: Before cropping, make sure the final dimensions match the size of the print media, whether it's a poster, flyer, or business card. Each type of print has its own standard sizes.
- Use CMYK color mode: For the best print quality, convert your image to CMYK color mode, as it's specifically designed for printing, whereas RGB is better for digital screens.
By following these guidelines, your cropped images will look sharp, professional, and ready for print—whether it's for a brochure, a poster, or any other printed material.
Also Read This: Understanding Why You Can’t Schedule a YouTube Video and Finding Solutions
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Cropping Images
Cropping is a simple task, but it’s easy to make mistakes that affect the quality of your image. Whether you're preparing an image for web, print, or social media, avoiding common pitfalls will save you time and frustration. Here are some frequent cropping errors and how to avoid them:
- Over-cropping: Cropping too tightly can remove important parts of your image, leaving it unbalanced or lacking context. Always leave enough room around your subject for breathing space.
- Ignoring aspect ratio: Changing the aspect ratio without considering the final platform can result in an awkward fit. If your image is for a specific platform (like Instagram or YouTube), stick to their preferred dimensions.
- Lowering resolution: Cropping reduces the number of pixels, so if you crop too much, you may end up with a low-resolution image. Always check the resolution after cropping, especially for print work.
- Neglecting focus: Cropping in a way that cuts out the focal point of your image can make it look less impactful. Ensure that the main subject is still prominent after cropping.
- Not considering the rule of thirds: Cropping without regard to composition can lead to a visually unbalanced image. Use the rule of thirds to enhance the composition.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your cropped images are clear, professional, and well-suited for their intended purpose.
Also Read This: Is YouTubing a Viable Career Choice for the Future
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions that people have when it comes to cropping images:
- Can I undo a crop after saving the image? It depends on the tool you’re using. Some software, like Photoshop, allows you to undo a crop if you saved the project as a file that keeps the cropping history. However, if you save an image in a compressed format (like JPEG), the crop is permanent.
- What’s the ideal resolution for cropped images for the web? A resolution of 72 DPI is typically enough for web images. However, you’ll also want to pay attention to pixel dimensions, making sure they fit the required size for the platform you’re using.
- Why does my image look pixelated after cropping? This happens when you crop too much of the image, reducing its resolution below an acceptable level. Try cropping less or using a higher-resolution source image to avoid this issue.
- Is there a difference between cropping for digital and print? Yes! For digital use, lower resolution and RGB color mode are fine, but for print, you need higher resolution (300 DPI) and CMYK color mode to ensure good quality.
Conclusion
Cropping is an essential tool for improving the composition and focus of your images, but it’s important to approach it thoughtfully. By understanding the right techniques, tools, and best practices, you can crop your images to fit any format—whether it’s for digital platforms or print. Remember to maintain the aspect ratio, avoid common mistakes, and use cropping creatively to enhance the visual impact of your work. With a little practice, cropping will become a quick and easy way to perfect your images every time.
 admin
admin








