Piecewise functions are like the chameleons of the math world—they can take on different forms based on the input! Essentially, a piecewise function is defined by multiple sub-functions, each of which applies to a specific interval of the function's domain. This allows for flexibility and a rich variety of behaviors in mathematical models, which can be quite useful in real-world applications.
In simpler terms, you can think of a piecewise function as a function that “pieces together” multiple functions to describe different scenarios. For example, imagine a tax system that has different rates depending on income levels; it's a perfect illustration of a piecewise function. The beauty of piecing together these functions is that they can represent complex relationships with relative ease and clarity. So, let’s dive deeper into what makes piecewise functions tick!
Understanding Graphs and Their Representation
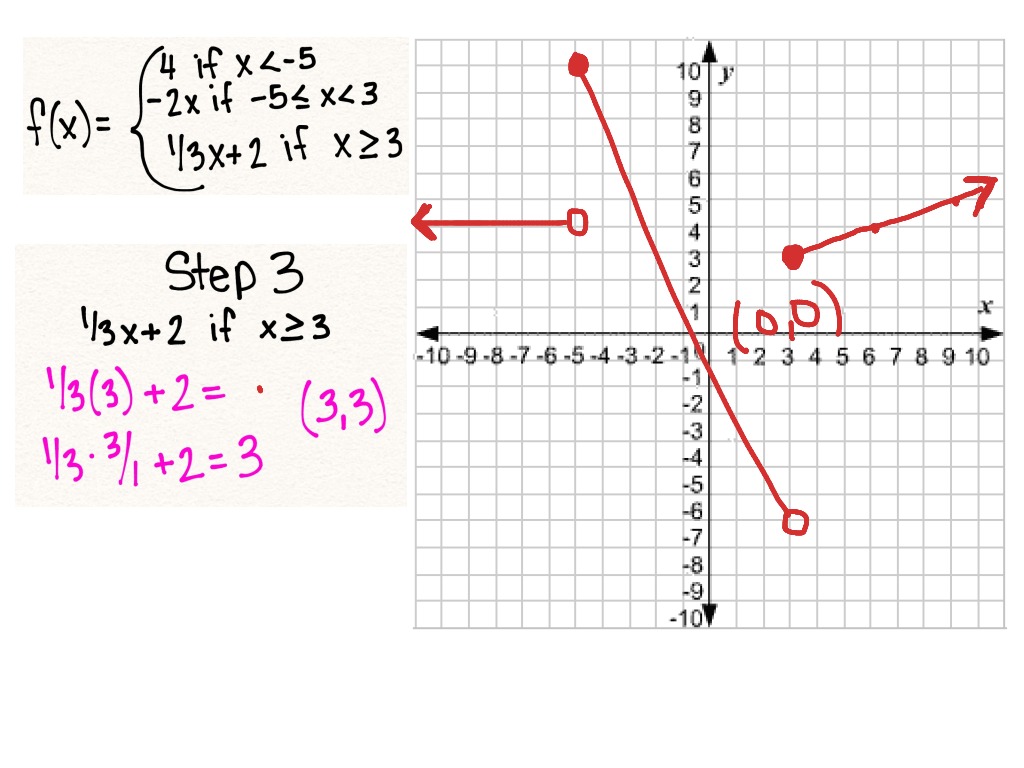
Graphs are powerful visual tools that help us understand and interpret functions at a glance. When we talk about piecewise functions, graphs become even more significant. They give us a way to visualize how a function behaves differently in different sections of its domain. Let’s break down some core concepts related to graphs and their representation, especially in the context of piecewise functions.
1. *Function Definition: A piecewise function is often represented like this: f(x) = {
- f1(x) for x
- f2(x) for a ≤ x
- f3(x) for x ≥ b
Where f1, f2, and f3 represent different equations or expressions for differing intervals.
2. Graph Interpretation: When you sketch a piecewise function, you typically see segments of lines or curves that connect only at specific points, often referred to as breakpoints. Each segment corresponds to a piece of the function, and identifying these breakpoints is crucial to understanding the overall behavior of the function.
3. Continuity and Discontinuity:* Piecewise functions can be continuous or discontinuous at their breakpoints. A continuous piecewise function means the graph has no gaps, while a discontinuous function has jumps or holes.
In summary, understanding how to read and interpret graphs is vital for creating and analyzing piecewise functions. Visual aids not only enhance our comprehension but also allow us to communicate complex ideas easily. So next time you see a piecewise graph, remember that it’s all about the beautiful interplay of different mathematical functions!
Identifying Segments of the Graph
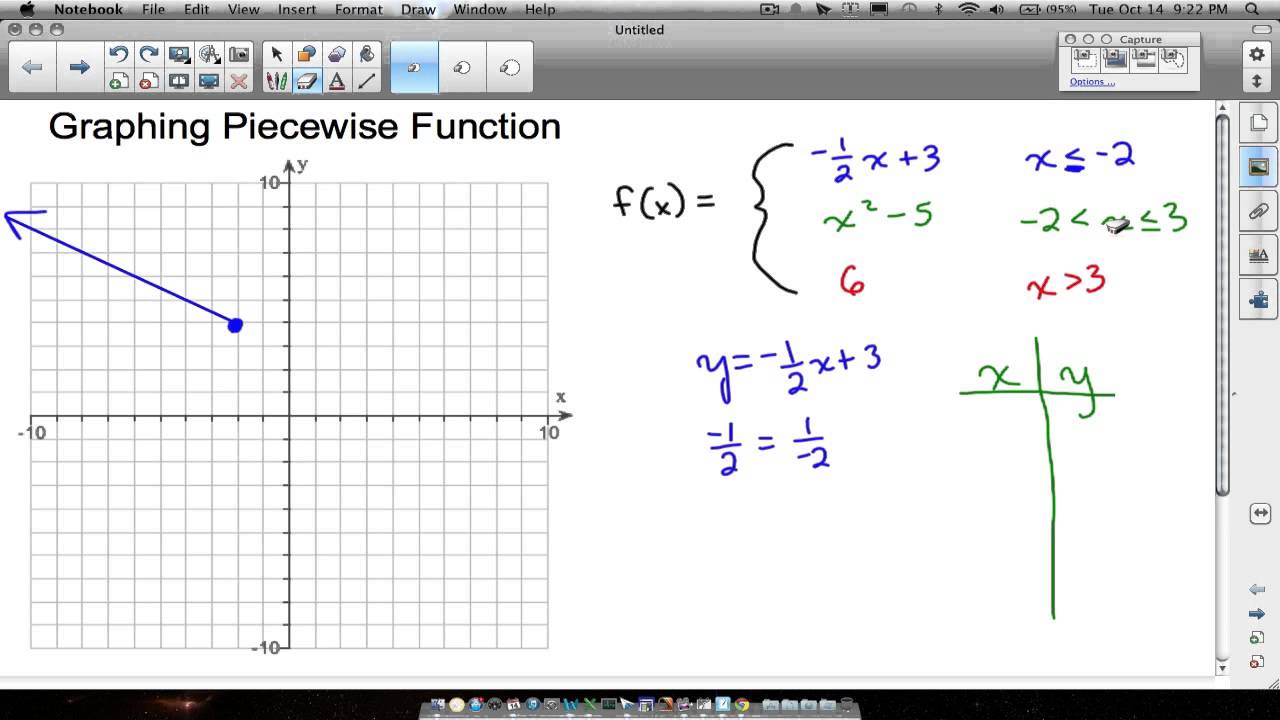
When it comes to creating a piecewise function, one of the first steps is to identify the segments of the graph. But what exactly does that mean? Well, a graph often consists of different portions, or segments, where the behavior of the function changes. These segments may consist of linear lines, curves, or even constant values.
To get started, take a close look at the graph. You want to notice where the function seems to change direction or where its pattern varies. Typically, this happens at specific points known as breakpoints. Here are some tips on how to identify those segments:
- Observe the slopes: Straight lines will have a constant slope, while curves will change their rate of rise or fall.
- Look for intersections: Points where the graph intersects the x-axis and y-axis can indicate significant changes in behavior.
- Identify flat sections: Any section of the graph that remains horizontal indicates a constant function over that interval.
- Check for discontinuities: Points where the graph jumps or has holes are crucial—these will inform how to define the function pieces.
Once you have tagged these segments, you're well on your way to assembling your piecewise function. Remember, each segment might represent a different rule, so take your time to ensure you've accurately captured all the changes!
Defining Each Piece of the Function
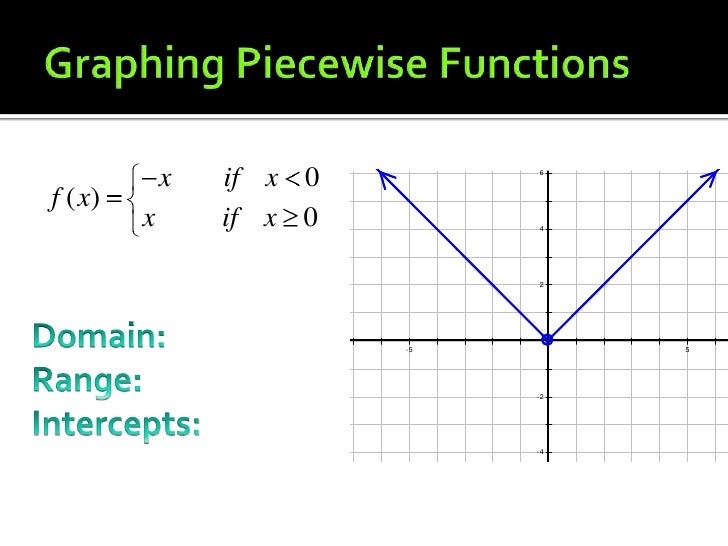
Now that you've identified the segments of your graph, it's time to define each piece of the function. This is where you’ll translate the visual elements of the graph into mathematical expressions. Don't worry if this sounds a bit daunting; it’s usually more straightforward than it might first appear!
First, let’s break it down step by step:
- Label Each Segment: Start by giving each segment a label based on the x-values it covers. For instance, if the first segment is valid from x = -2 to x = 1, you might label it as \(f(x)\) when \(x \in [-2, 1]\).
- Determine the Rule: Assess the segment's behavior. For linear segments, use the slope-intercept form \(y = mx + b\), while for more complex curves, you might need to use quadratic or other polynomial equations.
- Check Endpoints: Don't forget to consider whether the segment should include or exclude its endpoints. Use brackets for inclusive values and parentheses for exclusive ones.
For example, if you have a segment that increases linearly, you might define it like this:
f(x) = { 2x + 3, for x ∈ [-2, 1] x^2, for x ∈ (1, 4]}Remember, clarity is key. Make sure each piece is correctly defined, as this will form the basis of your complete piecewise function. And voilà! You've successfully defined each piece, setting the groundwork for expressing the entire function mathematically.
5. Writing the Piecewise Function
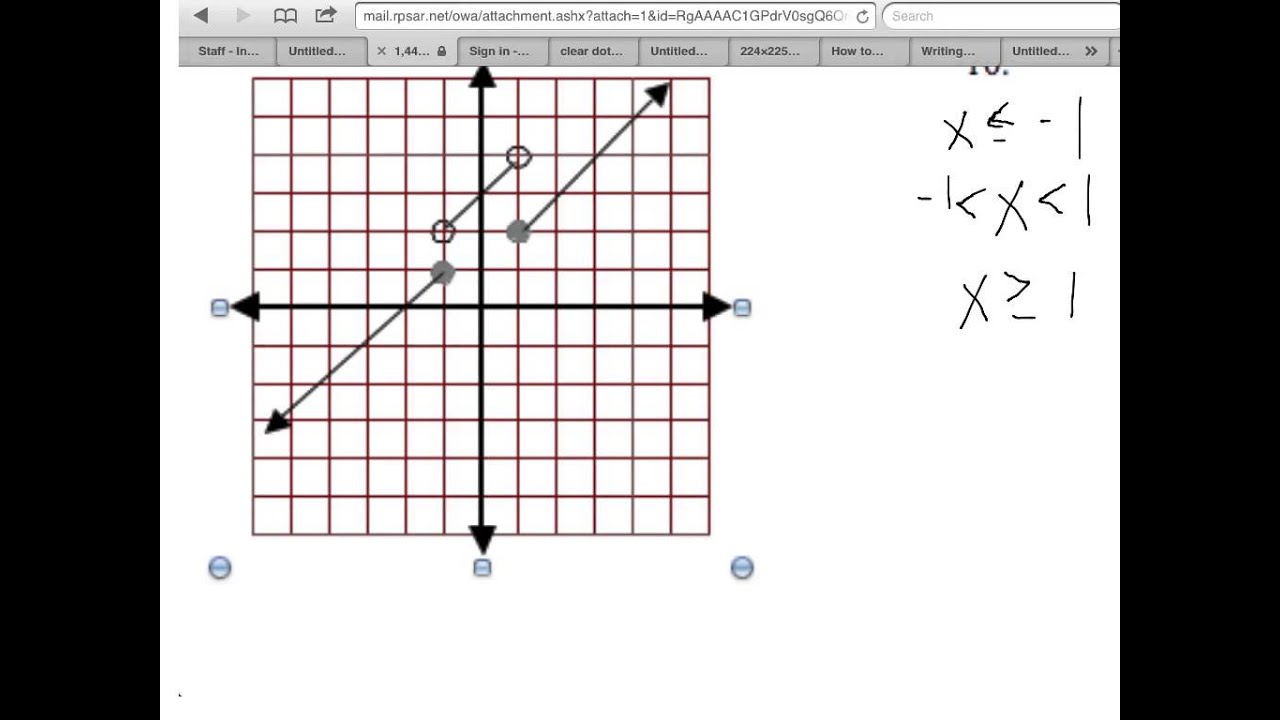
Creating a piecewise function from a graph might seem challenging, but it’s all about breaking things down! The key is to analyze each section of the graph individually and determine the rules that govern them. Here's a step-by-step approach to help you write a precise piecewise function.
First, take a good look at the graph and identify the different segments. Look for points where the graph changes direction or jumps—these are the points that typically define the boundaries of your function pieces.
- Identify the segments: For instance, does the graph rise steadily, fall, or remain constant in certain intervals?
- Determine the equations: For each segment, write down the equation that represents it. This could be linear, quadratic, or any other type of function. For example, a line can be expressed with the formula \(y = mx + b\), where \(m\) is the slope and \(b\) is the y-intercept.
- Define the intervals: Specify the domain for each piece. Use inequalities to indicate where each function applies. For example, if a function is linear from \(x = 0\) to \(x = 3\), you might write it as \(f(x) = mx + b\) for \(0 \leq x
Finally, put it all together in a neat piecewise function format:
f(x) = { equation1, if condition1 equation2, if condition2 ...}Make sure to double-check your intervals and equations match what you see on the graph. Voilà! You now have a piecewise function that describes the original graph.
6. Verifying the Function with the Graph
Now that you’ve crafted your piecewise function, it’s essential to verify that it accurately reflects the graph you started with. This ensures that your function effectively captures the behavior and the features of the original visual representation.
To do this, follow these validation steps:
- Graph the Function: Using a graphing tool (like Desmos or GeoGebra), input your piecewise function to visualize it. Make sure that the plotted graph matches the original one.
- Check Key Points: Identify critical points (like turning points, intersections, and endpoints) from the original graph and see if the corresponding values from your piecewise function provide the same output. This helps ensure you haven’t missed any important features.
- Evaluate at Boundaries: Examine the limits at each segment’s boundary. If your piecewise function is defined at a boundary, check if it equals the value of the graph at that point. For instance, if you're transitioning from one equation to another, does the value match?
Lastly, take a moment to review the characteristics of the graph: continuity, breaks, and slopes. If everything aligns, congratulations! You’ve successfully created a piecewise function that accurately represents the graph.
Verification is crucial because it not only confirms the accuracy of your work but also reinforces your understanding of piecewise functions and graph behaviors.
Examples and Practice Problems
Creating piecewise functions from graphs can seem daunting at first, but don’t worry—practice makes perfect! Here, we'll walk through a few examples and provide some practice problems for you to try on your own.
Example 1: A Simple Linear Function
Imagine a graph that consists of two lines:
- For x
- For x ≥ 0, the line is horizontal at y = 3.
This graph can be expressed as a piecewise function:
f(x) = { 2x, if x Example 2: A Quadratic Function
Now let's examine a quadratic function:
- For x
- For -1 ≤ x
- For x ≥ 2, the function falls back to a line with a slope of -2.
This leads to the piecewise representation:
f(x) = { -x + 4, if x Practice Problems
Try these on your own:
- Create a piecewise function from a graph with two linear segments, one for x
- Identify the piecewise function from a graph consisting of a linear piece and a quadratic piece.
- Examine a graph that involves a sinusoidal curve and linear segments, and write the corresponding function.
Feel free to share your answers, and let's see how you did!
Conclusion and Additional Resources
Understanding piecewise functions can greatly enhance your grasp of mathematics, especially when dealing with real-world scenarios where different rules apply to different situations. Throughout this guide, we've taken you through the steps of creating a piecewise function from a graph, and now you're equipped with practical examples and practice problems to solidify your understanding.
Here’s a quick recap of the key points:
- Piecewise functions combine multiple expressions based on the input value ranges.
- Graphs can reveal the transition points where one expression shifts to another.
- Practice is essential to mastering the creation of these functions!
For further learning, consider these resources:
| Resource | Type |
|---|---|
| Khan Academy | Video Lessons on Piecewise Functions |
| Desmos | Graphing Calculator for Visualization |
| Math is Fun | Interactive Lessons and Practice |
By utilizing these tools and consistently practicing, you'll find that creating piecewise functions becomes second nature to you. Best of luck on your mathematical journey!










