The journey of AI in image recognition is a fascinating story of technological advancements and innovative breakthroughs. This evolution has transformed the way images are processed and understood, leading to a myriad of applications that seemed like science fiction just a few decades ago.
The Early Stages: The initial steps in AI image recognition were primarily rule-based systems. These early models relied on specific, predefined algorithms to identify patterns in images. However, they lacked flexibility and were limited to very basic tasks.
Introduction of Neural Networks: The game-changer came with the introduction of neural networks, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), in the late 1980s. These networks were inspired by the human brain's visual cortex and could process images in layers, extracting features from simple to complex.
Advancements in Machine Learning: The 2000s witnessed significant improvements in machine learning algorithms. With the increase in computational power and the advent of big data, it became possible to train models on large datasets, leading to more accurate and efficient recognition systems.
Deep Learning Revolution: The real breakthrough, however, came with the advent of deep learning in the 2010s. Deep learning models, with their ability to learn and improve autonomously, took image recognition to new heights. They enabled the extraction of intricate patterns and details, far surpassing previous capabilities.
Recent Innovations: Today, AI image recognition is continuously evolving, integrating newer technologies like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and reinforcement learning. These advancements are not only improving accuracy but also expanding the range of applications.
| Decade | Key Advancement |
|---|
| 1980s | Introduction of Neural Networks |
| 2000s | Improvements in Machine Learning |
| 2010s | Deep Learning Developments |
| 2020s | Integration of Advanced AI Technologies |
The evolution of AI in image recognition is a testament to the relentless pursuit of more intelligent and adaptive technologies. From its rudimentary beginnings to the sophisticated systems of today, AI image recognition has not only grown in complexity but also in its ability to impact various sectors, ranging from healthcare to entertainment.
Understanding the Mechanism Behind AI Image Recognition
 AI image
AI image recognition is a complex process that involves several layers of computational logic and machine learning. At its core, this technology mimics human visual perception, but it does so at a speed and accuracy that far surpass human capabilities. Let's break down the key components and processes that underpin this fascinating technology.
1. Data Input and Preprocessing- Data Input: The process begins with the input of visual data, which can be in the form of images or videos.
- Preprocessing: This data is then preprocessed to enhance its quality and usability. Preprocessing may involve resizing, normalizing, and augmenting the images to make them suitable for analysis.
2. Feature Extraction- At this stage, AI algorithms, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), analyze the image to identify and extract various features. These features can range from basic elements like edges and colors to more complex patterns.
3. Classification and Recognition- After feature extraction, the AI model categorizes these features into different classes. This classification is based on the training the model has received, where it has learned to associate certain features with specific labels.
4. Deep Learning and Neural Networks- The heart of AI image recognition lies in deep learning and neural networks. These networks consist of multiple layers of nodes, or 'neurons', each designed to recognize different aspects of the image.
- The 'deep' in deep learning refers to the number of layers through which data is processed, allowing for the extraction of increasingly abstract and complex features.
| Layer Type | Function |
|---|
| Convolutional Layer | Extracts basic features like edges and textures |
| Pooling Layer | Reduces dimensionality, retaining essential information |
| Fully Connected Layer | Makes final classifications based on extracted features |
5. Training and Learning- The efficiency and accuracy of an AI image recognition model heavily depend on its training. This involves feeding large datasets of labeled images into the model, allowing it to learn and improve its recognition capabilities.
- The model uses algorithms like backpropagation to adjust and refine its parameters, continually enhancing its ability to recognize and classify images accurately.
In summary, AI image recognition involves a sophisticated interplay of data processing, feature extraction, and machine learning, all orchestrated by deep learning models and neural networks. This mechanism allows AI to not only 'see' but also understand and interpret visual data in a way that is transforming numerous industries and applications.
Applications of AI Image Recognition in Various Industries
AI image recognition has permeated various sectors, revolutionizing how tasks are performed and opening new avenues for innovation and efficiency. Let's explore some of the key industries where AI image recognition is making a significant impact.
Healthcare- Diagnostic Imaging: AI helps in analyzing medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, assisting in early and accurate diagnosis of diseases like cancer, fractures, and neurological disorders.
- Pathology: In pathology, AI aids in analyzing tissue samples, detecting abnormalities, and providing insights for precise treatment strategies.
Retail- Customer Experience: Retailers use AI image recognition for facial recognition to personalize shopping experiences, manage inventory through image-based tracking, and enhance security.
- Visual Search: AI enables customers to search for products using images, making the shopping experience more intuitive and efficient.
Automotive- Autonomous Vehicles: AI image recognition is crucial in self-driving cars, helping them to recognize and interpret road signs, obstacles, and other vehicles to navigate safely.
Security and Surveillance- Facial Recognition: Widely used for security purposes, AI image recognition can identify individuals in crowds, enhance border control, and monitor public spaces.
Manufacturing- Quality Control: In manufacturing, AI image recognition is used for inspecting products, detecting defects, and ensuring quality control.
Agriculture- Crop Monitoring: AI helps in monitoring crop health, detecting pests and diseases, and analyzing soil conditions through aerial images.
| Industry | Application |
|---|
| Healthcare | Diagnostic Imaging, Pathology |
| Retail | Customer Experience, Visual Search |
| Automotive | Autonomous Vehicles |
| Security | Facial Recognition |
| Manufacturing | Quality Control |
| Agriculture | Crop Monitoring |
These applications are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the potential of AI image recognition. As technology advances, its impact is bound to expand, offering even more innovative solutions across diverse industries.
Comparing AI Image Recognition with Human Perception
The comparison between AI image recognition and human perception reveals fascinating insights into the capabilities and limitations of both. While AI has made significant strides in interpreting and analyzing visual data, understanding how it compares to the human eye and brain offers a broader perspective on its current state and future potential.
Speed and Accuracy- AI Image Recognition: AI systems can process and analyze images at an incredibly fast rate, often surpassing human speed. Their accuracy, particularly in tasks like pattern recognition and anomaly detection, is consistently high, thanks to machine learning and vast data sets.
- Human Perception: Humans process visual information more slowly and are more prone to errors, especially in repetitive or detailed-oriented tasks.
Complexity and Contextual Understanding- AI Image Recognition: AI struggles with understanding the context and complex nuances of images. It interprets what it 'sees' based on data and algorithms, which can sometimes lead to misinterpretation, especially in ambiguous situations.
- Human Perception: Humans excel at understanding context, emotions, and subtleties in images. Our brains can interpret complex scenes and make intuitive judgments that AI currently cannot match.
Learning and Adaptability- AI Image Recognition: AI systems require extensive training with large data sets to accurately recognize and classify images. They are not inherently adaptable and require retraining to accommodate new information or changes.
- Human Perception: Humans can learn and adapt to new visual information more dynamically. We can recognize patterns and make connections with limited data and experience.
| Aspect | AI Image Recognition | Human Perception |
|---|
| Speed and Accuracy | High speed, high accuracy | Slower, prone to errors |
| Complexity and Context | Limited contextual understanding | Excellent contextual understanding |
| Learning and Adaptability | Requires extensive training | Naturally adaptable |
In conclusion, while AI image recognition offers advantages in speed and accuracy, human perception still leads in understanding complexity, context, and adaptability. The ongoing development in AI aims to bridge these gaps, aspiring to create systems that can not only see but also understand images in a way that is more akin to human perception.
Despite its impressive advancements, AI image recognition technology still faces significant challenges and limitations. Understanding these hurdles is essential for both appreciating the current capabilities of AI and recognizing the areas that require further development.
Data Dependence and Bias- Data Quality and Quantity: AI image recognition systems require large volumes of data for training. The quality and diversity of this data directly impact the system's effectiveness, potentially leading to biases and inaccuracies in less represented categories.
- Bias in Data Sets: Bias in training data can lead AI systems to develop skewed perceptions, resulting in discriminatory or unfair outcomes, especially in sensitive applications like facial recognition.
Computational Complexity and Resource Requirements- High Computational Power: Advanced AI image recognition systems demand significant computational power, which can be costly and energy-intensive.
- Resource Intensive: The need for extensive data storage and processing capabilities means that these systems are often resource-intensive, posing challenges for scalability and environmental sustainability.
Contextual and Nuanced Understanding- AI systems generally lack the nuanced understanding of context that humans possess. This can lead to misinterpretations, especially in complex or ambiguous scenarios.
Adaptability and Generalization- AI models are often trained on specific datasets and may struggle to adapt to new, unseen scenarios or generalize their learning across different contexts.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|
| Data Dependence and Bias | Requires extensive, diverse data; prone to biases. |
| Computational Complexity | Demanding in terms of computational power and resources. |
| Contextual Understanding | Limited in interpreting complex, ambiguous scenarios. |
| Adaptability and Generalization | Challenges in adapting to new scenarios and generalizing across different contexts. |
In summary, while AI image recognition is a powerful tool, it is not without its challenges. Addressing these issues requires continuous research and development, coupled with a mindful approach to the ethical implications of this technology.
The Future of AI Image Recognition: Trends and Predictions
The field of AI image recognition is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advances and increasing demand across various sectors. Let's explore some key trends and predictions shaping the future of this exciting domain.
Enhanced Computational Efficiency- Future AI systems are expected to become more computationally efficient, enabling faster processing with lower resource requirements.
- Advancements in hardware, like specialized AI chips, are predicted to facilitate this efficiency, making AI image recognition more accessible and scalable.
Improved Accuracy and Contextual Understanding- Continuous improvements in algorithms will likely lead to higher accuracy rates, even in complex and nuanced scenarios.
- Developments in deep learning and neural networks could enhance the contextual and emotional understanding of AI, making it more akin to human perception.
Expansion in Diverse Applications- AI image recognition is set to expand into new industries, including more specialized healthcare applications, environmental monitoring, and personalized education.
Addressing Ethical and Privacy Concerns- With growing awareness of privacy and ethical implications, future developments will likely include more robust frameworks and regulations to ensure responsible use.
Integration with Other AI Technologies- Integration with other AI domains such as natural language processing (NLP) and predictive analytics is expected, leading to more sophisticated and multi-dimensional AI systems.
| Trend/Prediction | Impact |
|---|
| Computational Efficiency | More accessible, scalable AI image recognition. |
| Accuracy and Contextual Understanding | More precise and human-like image interpretation. |
| Diverse Applications | Broader implementation across various sectors. |
| Ethical and Privacy Concerns | Increased focus on responsible AI usage. |
| Integration with Other AI Tech | Development of multi-dimensional AI systems. |
These trends indicate a future where AI image recognition not only becomes more advanced and widespread but also more ethically aligned and integrated with other technologies, opening new possibilities and applications.
How HDStockImages Leverages AI for Free Image Generation
HDStockImages is at the forefront of utilizing AI technology for
free image generation, offering users a unique and powerful tool to create high-quality images. This section delves into how HDStockImages harnesses AI for this innovative service.
Integration of Advanced AI Algorithms- HDStockImages integrates cutting-edge AI algorithms, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), to generate diverse and high-resolution images.
- These AI models are trained on vast datasets, enabling the creation of images that cater to a wide range of themes and styles.
User-Friendly Interface for Customization- The platform provides a user-friendly interface, allowing users to input text descriptions or keywords. The AI then interprets these inputs to generate corresponding images.
- This feature empowers users to create custom images without the need for advanced design skills.
Real-Time Image Generation- HDStockImages leverages AI for real-time image generation, significantly reducing the time and effort required compared to traditional image creation methods.
Continuous Learning and Improvement- The AI system continuously learns from user inputs and feedback, improving its accuracy and output quality over time.
Addressing Copyright Issues- By generating unique images, HDStockImages helps users avoid copyright issues often associated with stock photos.
| Feature | Description |
|---|
| AI Algorithms | Use of GANs and other advanced models for diverse image creation. |
| User Interface | Simple, intuitive interface for custom image generation. |
| Real-Time Generation | Efficient creation of images, saving time and resources. |
| Continuous Improvement | Adaptive learning from user interactions for enhanced performance. |
| Copyright Solutions | Unique image generation to avoid legal issues. |
In summary, HDStockImages' use of AI for
free image generation represents a significant advancement in the field of digital imagery. It not only simplifies the image creation process but also ensures high-quality, unique, and customizable outputs, catering to the diverse needs of its users.
FAQs on AI Image Recognition
Here are some frequently asked questions about AI image recognition that can help clarify common queries and misconceptions:
- What is AI image recognition?
AI image recognition is a technology that allows computers to interpret and understand visual data from the world around them, similar to the way humans visually perceive their environment.
- How does AI recognize images?
AI uses algorithms, often based on neural networks, to process and analyze visual data. These algorithms can identify patterns, shapes, and features in images to recognize objects, faces, scenes, and more.
- Is AI image recognition better than human perception?
While AI image recognition can process and analyze images faster and more consistently than humans, it lacks the nuanced understanding and contextual interpretation that humans have.
- Can AI image recognition be biased?
Yes, if the data used to train AI models is biased, the AI system can inherit these biases, leading to skewed results and unfair outcomes, particularly in sensitive applications.
- What are some common applications of AI image recognition?
AI image recognition is used in various fields, including healthcare, security, retail, automotive, and entertainment, for tasks such as facial recognition, object detection, and automated image tagging.
- How is AI image recognition used in healthcare?
In healthcare, AI image recognition can analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs to assist in diagnosing diseases, planning treatments, and monitoring patient progress.
- Are there any privacy concerns with AI image recognition?
Yes, applications like facial recognition have raised significant privacy concerns. There's a growing call for regulations to ensure ethical use and protect individual privacy.
- What is the future of AI image recognition?
The future of AI image recognition involves improved accuracy, computational efficiency, and integration with other AI technologies. Ethical and privacy considerations are also expected to play a significant role in its evolution.
Conclusion: The Impact of AI Image Recognition on Digital Imagery
As we have explored, AI image recognition has significantly transformed the landscape of digital imagery. This technology has not only enhanced the capabilities of various industries but also introduced new dimensions in the way we interact with and interpret visual information.AI image recognition has provided tools that enable more efficient, accurate, and detailed analysis of images, surpassing human capabilities in many aspects. In industries such as healthcare, security, and retail, it has become an invaluable asset, improving diagnostics, enhancing surveillance, and personalizing customer experiences.However, this rapid advancement comes with its own set of challenges. Concerns regarding privacy, ethical implications, and potential biases in AI models are critical issues that need addressing. As the technology continues to evolve, it is crucial to strike a balance between leveraging its benefits and mitigating its risks.The future of AI image recognition promises even greater integration into our daily lives and industries, with trends pointing towards more sophisticated, efficient, and ethically aligned developments. It holds the potential not only to revolutionize how we process and utilize visual information but also to reshape our understanding of AI's role in the digital era.In conclusion, the impact of AI image recognition on digital imagery is profound and far-reaching. As we continue to innovate and navigate the complexities of this technology, it is poised to open up new horizons and possibilities, redefining the boundaries of what is achievable in the realm of digital imagery.
 AI image recognition is a complex process that involves several layers of computational logic and machine learning. At its core, this technology mimics human visual perception, but it does so at a speed and accuracy that far surpass human capabilities. Let's break down the key components and processes that underpin this fascinating technology.1. Data Input and Preprocessing
AI image recognition is a complex process that involves several layers of computational logic and machine learning. At its core, this technology mimics human visual perception, but it does so at a speed and accuracy that far surpass human capabilities. Let's break down the key components and processes that underpin this fascinating technology.1. Data Input and Preprocessing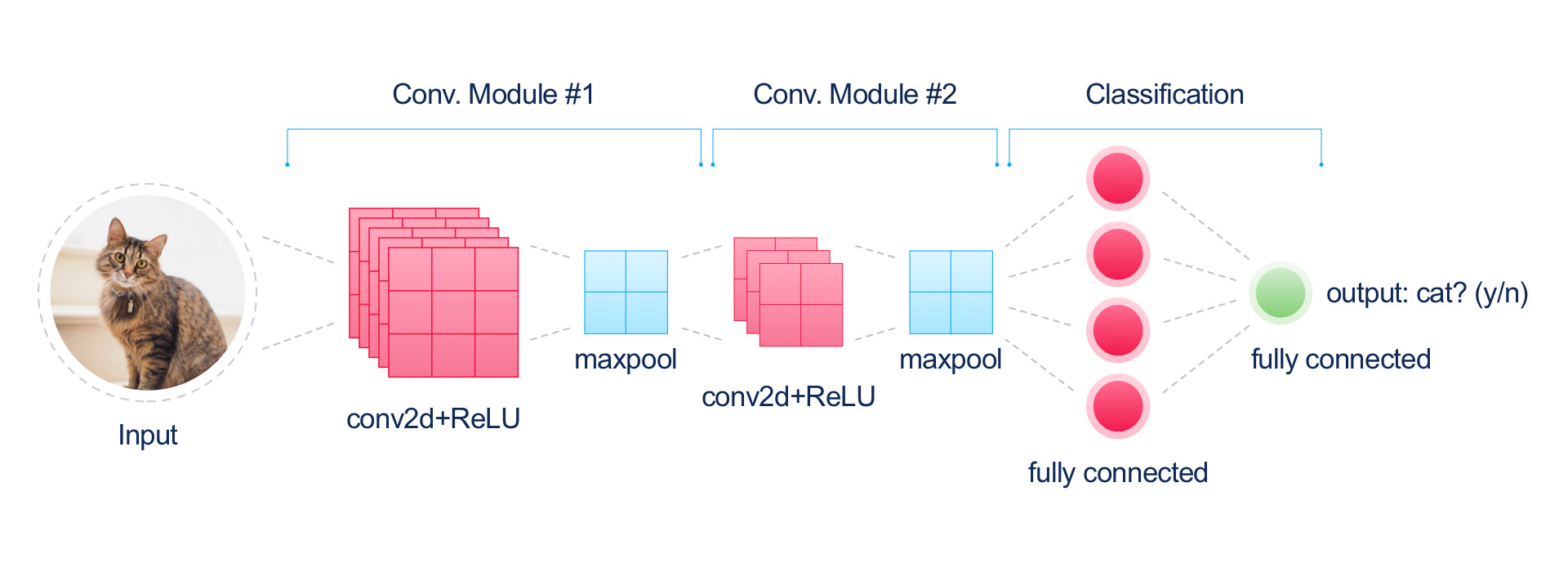
 admin
admin