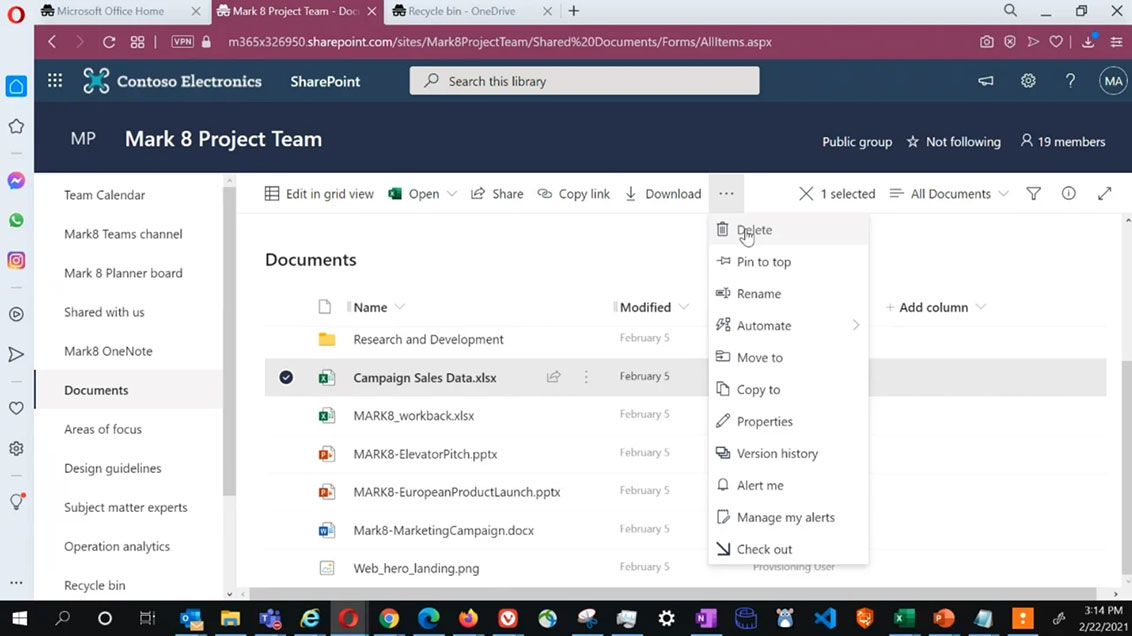
Deleting documents in
Microsoft 365 involves more than just removing files; it's a nuanced process that impacts data security and storage management. Let's delve into the key aspects of document deletion in
Microsoft 365:
1. Deletion Methods
Microsoft 365 offers multiple methods for deleting documents, catering to various user preferences. Users can employ the traditional 'Delete' button, right-click options, or use keyboard shortcuts like 'Ctrl + D.' Each method initiates the deletion process, but users should be mindful of their chosen approach to ensure the intended files are removed.
2. OneDrive and SharePoint Considerations
Document deletion in
Microsoft 365 is intricately tied to OneDrive and SharePoint. Users need to understand how deleting a document in OneDrive differs from deleting it in SharePoint. OneDrive deletions may move the document to the Recycle Bin, while SharePoint deletions can be subject to site-specific retention policies.
3. Document Versions
Document deletion may also involve considerations for version history. If versioning is enabled, deleting the current version may not remove previous iterations. Users should be aware of versioning settings and take appropriate actions to manage document history effectively.
4. Retention Policies
Microsoft 365's retention policies play a crucial role in document disposal. Organizations can define policies that govern the retention and deletion of documents based on specific criteria. Understanding and configuring these policies ensures compliance with data governance regulations and internal data management practices.
5. Recoverability from Recycle Bin
Deleted documents often find their way into the Recycle Bin, offering a safety net for accidental deletions. Users can recover documents from the Recycle Bin, but it's essential to know that items may have a limited retention period before permanent deletion.
6. Permanent Deletion
While the Recycle Bin provides a chance for recovery, permanent deletion is a decisive step. Users must comprehend the implications of permanently deleting documents, as this action typically removes files beyond the scope of recovery, emphasizing the importance of careful consideration before executing such actions.
7. Best Practices for Secure Deletion
Implementing best practices for secure document deletion is crucial. This includes regularly reviewing and disposing of unnecessary documents, educating users on proper deletion procedures, and staying informed about updates to
Microsoft 365's document disposal features.By understanding these nuances, users can navigate the document deletion process in
Microsoft 365 with confidence, ensuring the efficient management and security of digital assets.
Retention Policies
Retention policies in
Microsoft 365 are pivotal for organizations aiming to manage their data effectively, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and internal data governance policies. Let's explore the intricacies of retention policies and their impact on document retention and disposal:
1. Definition and Purpose
Retention policies define the lifespan of documents within
Microsoft 365. They specify how long documents should be retained and what actions should be taken when the retention period expires. The primary purpose is to automate the management of data lifecycle, reducing the risk of unintentional data retention and facilitating regulatory compliance.
2. Policy Components
A retention policy consists of key components, including the retention label, retention settings, and the retention action. The retention label defines the classification of documents, while settings determine the duration of retention. The retention action specifies whether to retain or delete documents once the retention period concludes.
3. Applying Retention Policies
Organizations can apply retention policies to specific sites, mailboxes, or individual documents. This flexibility allows for granular control over data retention based on business needs and regulatory requirements. Users can assign retention labels manually or use automated processes to apply labels based on predefined conditions.
4. Preservation Lock
Retention policies may include a preservation lock, preventing users from modifying or deleting documents subject to a legal hold. This feature ensures the preservation of relevant data for legal or compliance purposes, safeguarding organizations during legal proceedings.
5. In-Place Holds
In addition to retention policies, organizations can implement in-place holds to preserve specific versions of documents. This functionality is particularly useful in scenarios where document versions need to be retained for audit or compliance purposes, even if the retention policy would otherwise delete them.
6. Monitoring and Auditing
Regular monitoring and auditing of retention policies are essential to ensure compliance and identify any potential issues.
Microsoft 365 provides reporting tools to track the application of retention policies, helping organizations stay informed about their data management practices.
7. Collaboration with Compliance Center
The
Microsoft 365 Compliance Center facilitates the creation, management, and monitoring of retention policies. Organizations can leverage this centralized hub to streamline compliance efforts and ensure consistent application of retention policies across the entire
Microsoft 365 environment.Understanding and effectively implementing retention policies in
Microsoft 365 is crucial for organizations seeking to strike the right balance between data retention and disposal, aligning with their overarching data governance strategies.
Recycle Bin Usage
The Recycle Bin in
Microsoft 365 serves as a safety net for users, offering a mechanism for temporarily storing deleted documents before their final disposal. Understanding how to effectively use the Recycle Bin is essential for users seeking to recover accidentally deleted files and manage their digital workspace efficiently.
1. Accessing the Recycle Bin
To access the Recycle Bin, users can navigate to the 'Recycle Bin' or 'Deleted Items' folder within specific applications such as OneDrive or Outlook. The Recycle Bin consolidates deleted items, providing a centralized location for potential recovery.
2. Retention Period
Items placed in the Recycle Bin are retained for a specific period, after which they may be permanently deleted. The retention period varies based on the organization's settings and can be customized. Users should be aware of this timeframe to ensure timely recovery of valuable documents.
3. Recovery Process
Restoring documents from the Recycle Bin is a straightforward process. Users can select the desired items, right-click, and choose the 'Restore' option. Alternatively, they can drag and drop items back to their original locations. This ensures a quick and efficient recovery process for accidentally deleted files.
4. Bulk Deletion and Recovery
The Recycle Bin allows users to perform bulk deletion and recovery actions. This is particularly useful when managing large sets of deleted documents. Users can select multiple items and apply actions such as 'Delete' or 'Restore' to streamline the process.
5. Recycle Bin in SharePoint
SharePoint also has its own Recycle Bin, separate from the Recycle Bin in OneDrive or other applications. Users managing documents in SharePoint should be familiar with the unique Recycle Bin associated with the SharePoint site. Items deleted in SharePoint may follow site-specific retention policies.
6. Monitoring and Emptying the Recycle Bin
Regularly monitoring the contents of the Recycle Bin is crucial. Users should periodically review and empty the Recycle Bin to free up storage space and ensure compliance with data retention policies. Organizations can set automated processes for Recycle Bin emptying based on specific criteria.
7. Best Practices for Recycle Bin Management
Implementing best practices for Recycle Bin usage involves educating users on proper deletion procedures, promoting regular reviews of the Recycle Bin contents, and providing guidelines on when to empty the Recycle Bin. Emphasizing these practices contributes to a more organized and secure digital workspace.Effectively leveraging the Recycle Bin in
Microsoft 365 is a fundamental skill for users, ensuring the recovery of valuable documents and maintaining a streamlined data management process.
Permanent Deletion
Permanent deletion in Microsoft 365 is a decisive step with far-reaching consequences. It involves the irreversible removal of documents, emphasizing the importance of careful consideration before initiating this process. Let's explore the nuances of permanent deletion and its implications:
1. Irreversibility and Caution
Permanent deletion means there is no recourse for recovering deleted documents. Users should exercise caution and ensure they genuinely no longer need the files before opting for permanent deletion. This step is irreversible and eliminates any possibility of recovery from the Recycle Bin.
2. Methods of Permanent Deletion
Microsoft 365 provides multiple methods for permanently deleting documents. Users can choose the 'Permanently Delete' option in the Recycle Bin or use keyboard shortcuts to bypass the Recycle Bin entirely. Understanding the available methods empowers users to select the most appropriate approach based on their workflow.
3. Retention Policies and Permanent Deletion
Organizations with specific retention policies must align permanent deletion practices with these policies. Some documents may be subject to extended retention periods, legal holds, or preservation requirements. Users should be aware of how retention policies interact with permanent deletion to avoid unintentional data loss.
4. Secure Deletion Practices
Secure deletion practices are crucial when permanently removing sensitive or confidential documents. Microsoft 365 offers features such as data loss prevention (DLP) policies, which can prevent the accidental permanent deletion of classified or regulated information. Implementing these practices adds an extra layer of security to the permanent deletion process.
5. Automating Permanent Deletion
Organizations can streamline the permanent deletion process by automating it through scripts or workflows. This is particularly useful for managing large volumes of data or adhering to specific data disposal schedules. Automation ensures consistency and reduces the likelihood of human error during the permanent deletion process.
6. Communication and Training
Effective communication and user training are essential aspects of permanent deletion management. Organizations should communicate clear guidelines on when permanent deletion is appropriate and provide training to users on the associated risks and best practices. This ensures a uniform understanding of the importance of responsible data management.
7. Auditing and Accountability
Regular auditing of permanent deletion actions adds an accountability layer to the process. Organizations can track who initiated permanent deletions, when they occurred, and the types of documents affected. This information is valuable for compliance purposes and internal governance.Permanent deletion in Microsoft 365 demands careful attention to avoid unintended data loss. By understanding the intricacies of this process and incorporating best practices, users and organizations can navigate permanent deletion with confidence and responsibility.
Data Security Measures
Data security is a paramount concern in the digital landscape, and implementing robust measures within Microsoft 365 is essential to safeguard sensitive information. Let's explore key data security measures that users and organizations can adopt to enhance the protection of their data:
1. Encryption Protocols
End-to-end encryption: Implementing end-to-end encryption ensures that data remains encrypted throughout its lifecycle, from creation to storage and transmission. This prevents unauthorized access and protects the confidentiality of sensitive information.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA implementation: Enforcing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing Microsoft 365 services. This mitigates the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC policies: Utilizing role-based access control allows organizations to define and manage user permissions based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that users have the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of inadvertent data exposure or manipulation.
4. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP policies: Implementing DLP policies helps prevent the accidental or intentional disclosure of sensitive data. These policies can be configured to monitor and restrict the sharing of confidential information, providing an additional layer of protection against data leaks.
5. Threat Intelligence Integration
Integration with threat intelligence: Leveraging threat intelligence services enhances the ability to identify and respond to emerging cybersecurity threats. Microsoft 365 allows organizations to integrate with threat intelligence feeds, enabling proactive measures against evolving security risks.
6. Regular Security Audits
Periodic security audits: Conducting regular security audits within Microsoft 365 is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with security policies. Audits can encompass user activities, access logs, and configurations to maintain a robust security posture.
7. Incident Response Planning
Incident response planning: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place is essential for effectively addressing security incidents. This plan should include procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security breaches, minimizing the impact on data integrity and availability.
8. Employee Training and Awareness
Security awareness programs: Educating employees on security best practices is a fundamental aspect of data security. Training programs can cover topics such as phishing awareness, secure document handling, and reporting suspicious activities, fostering a security-conscious organizational culture.
9. Data Backups and Recovery
Regular data backups: Implementing regular data backups ensures that organizations can recover from data loss events, whether caused by security incidents, system failures, or human error. Backups should be stored securely and tested for reliability.By incorporating these data security measures, users and organizations can establish a robust defense against potential threats, protect sensitive information, and foster a secure computing environment within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
FAQ
Explore the frequently asked questions about document disposal in Microsoft 365 to enhance your understanding of the process and address common queries:
Q1: What happens when I delete a document in Microsoft 365?
A: When you delete a document, it is typically moved to the Recycle Bin. From there, you have the opportunity to recover it. However, the specific behavior may vary depending on your settings and whether you are using OneDrive, SharePoint, or other applications.
Q2: Can I permanently delete a document without sending it to the Recycle Bin?
A: Yes, you can permanently delete a document by bypassing the Recycle Bin. This action is irreversible and should be performed with caution, as the document won't be recoverable.
Q3: How do retention policies affect document disposal?
A: Retention policies in Microsoft 365 determine how long documents are retained before disposal. These policies can be based on various criteria, and understanding them is crucial to compliant data management.
Q4: Is it possible to recover documents from the Recycle Bin after they've been permanently deleted?
A: No, once a document is permanently deleted, it cannot be recovered from the Recycle Bin. Permanent deletion means the document is removed beyond the point of recovery.
Q5: How can I automate the document disposal process in Microsoft 365?
A: Automation can be achieved through scripting or workflows. Organizations can set up automated processes to delete documents based on specific criteria or schedules, streamlining data management.
Q6: What measures can I take to secure the document disposal process?
A: Secure document disposal involves practices such as implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and data loss prevention. Educating users, conducting security audits, and having an incident response plan also contribute to a secure process.
Q7: How long are documents retained in the Recycle Bin?
A: The retention period for documents in the Recycle Bin varies and can be customized based on organizational settings. It's essential to be aware of this timeframe to ensure timely recovery if needed.
Q8: Can I recover multiple documents simultaneously from the Recycle Bin?
A: Yes, most Microsoft 365 applications allow users to select and recover multiple documents at once from the Recycle Bin, streamlining the recovery process for efficiency.These FAQs provide insights into common concerns related to document disposal in Microsoft 365. If you have additional questions, feel free to reach out for further clarification.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of document disposal in Microsoft 365, it's evident that this process is more than a routine task—it's a critical aspect of data management with significant implications for security and compliance. Let's recap the key takeaways:
Emphasis on Responsible Data Management
Document disposal goes beyond mere deletion; it demands a thoughtful and responsible approach. Users must be mindful of the methods they choose, considering the impact on data security, recoverability, and compliance.
Retention Policies as Guardians of Data
Retention policies emerge as powerful tools in the management of document lifecycles. Organizations benefit from defining policies that align with their specific needs, ensuring data is retained or disposed of in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Recycle Bin as a Safety Net
The Recycle Bin acts as a safety net for accidental deletions, providing users with an opportunity to recover documents. Understanding its usage, retention periods, and recovery processes is crucial for maintaining a streamlined and secure digital workspace.
Permanent Deletion Requires Caution
Permanent deletion is irreversible and demands caution. Users should be well-informed about the consequences and take deliberate steps when opting for this method. Integrating secure deletion practices and aligning with retention policies is vital.
Comprehensive Data Security Measures
Enhancing data security within Microsoft 365 involves a multi-faceted approach. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and regular audits contribute to a robust defense against potential threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The Microsoft 365 environment evolves, and so should our understanding of its features and capabilities. Regular training, staying informed about updates, and adapting security measures accordingly are integral to maintaining a resilient and secure digital ecosystem.By navigating the intricacies of document disposal in Microsoft 365 with a clear understanding of its nuances, users and organizations can not only streamline their data management processes but also fortify their defenses against the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.