Who would have thought that potatoes, a staple food item, could double as a source of electricity? It might sound a bit whimsical, but generating electricity from potatoes has captured the attention of science enthusiasts and DIY aficionados alike. In a world that's increasingly focused on renewable energy, this quirky experiment offers a fun and educational way to understand basic electrical principles. In this post, we'll dive into what bioelectricity is all about and how you can create your own potato-powered battery using easy Dailymotion videos as guidance. Ready to explore the electrifying world of potatoes? Let’s get started!
Understanding the Concept of Bioelectricity
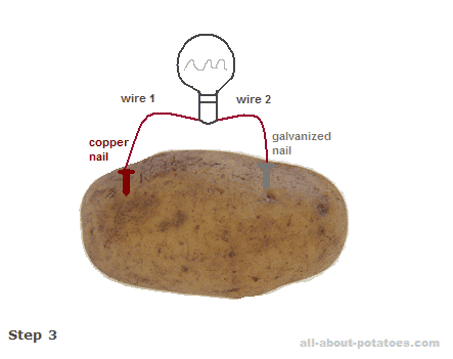
Bioelectricity refers to the electrical currents produced by living organisms. This phenomenon is not limited to potatoes, but they offer a fascinating example when it comes to energy production. Let’s break down the process and see how it relates to our starchy friends.
- What is Bioelectricity? – At its core, bioelectricity is the energy produced by biological processes, including chemical reactions within cells. In potatoes, the starch and other compounds can facilitate electrical reactions.
- Potatoes as Electrolytes: Potatoes contain a certain amount of water and electrolytes (like ions), both of which are crucial for conducting electricity. When you cut a potato, the chemical compounds inside start to interact, and these interactions can create a flow of electrons when connected with metal electrodes.
- How It Works: By inserting two different types of metal electrodes, such as copper and zinc, into the potato, you create a simple electrochemical cell. The chemical reaction between the metals and the potato’s internal components allows electrons to flow, thus generating a small electrical current.
- The Voltage Factor: A single potato battery can produce about 0.5 to 0.7 volts. While you may not be running your home on potato power, it’s enough to light up a small LED or power a simple circuit!
Understanding bioelectricity through potato experiments is a simple yet effective way to grasp key concepts in physics and chemistry. It combines educational fun with a pinch of creativity, pushing us to think outside the box—or in this case, the kitchen! So grab your potatoes and get ready to spark some interest in science!
Also Read This: Using Dailymotion to Draw and Understand Complex Geometrical Figures
3. Materials Needed for the Potato Battery Experiment

Before diving into the fun world of potato batteries, it's essential to gather the right materials. Here’s what you’ll need:
- 2 Medium-sized Potatoes: The star of our experiment! Any regular potato will do, but ideally, choose fresh ones to ensure good conductivity.
- 2 Copper Coins or Strips: These will act as one of the electrodes. If you don’t have coins, copper wire will work just fine!
- 2 Zinc Nails or Galvanized Nails: You’ll need these to serve as the second electrode. They’ll help create a chemical reaction with the copper.
- Insulated Wires: You’ll need a couple of these to connect the electrodes to a small device, like an LED light or a digital clock.
- A Small Light Bulb or LED: This will be your load, which shows the electricity produced by your potato battery. It’s a great visual indicator of your success!
- A Knife (for poking): Use this carefully to make holes in the potatoes for inserting the electrodes.
- Multimeter (optional): If you want to measure the voltage produced, a multimeter can be handy.
Gathering these materials should be a fun outing to the kitchen or your local hardware store. It’s always nice to prepare together with friends or family—after all, science is better when shared!
Also Read This: How to Make Cheese – DIY Cheese Making Tips on Dailymotion
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Electricity from Potatoes
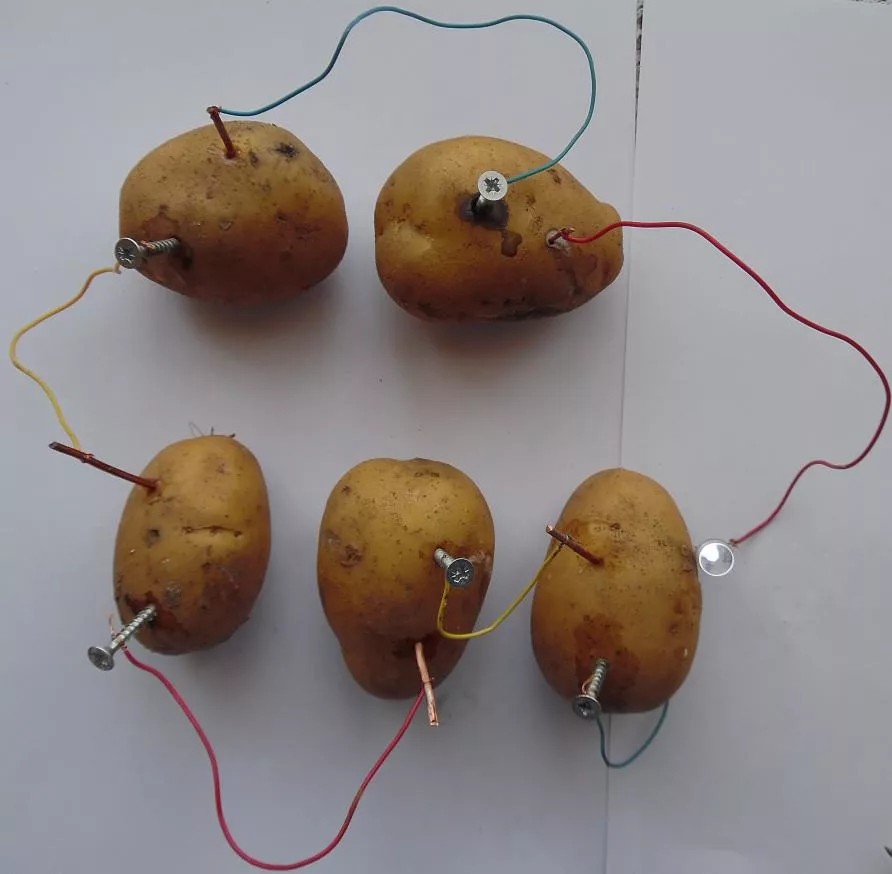
Now that you have your materials ready, let's jump into creating your very own potato battery! It’s a straightforward process, and you’ll be amazed at the science behind it.
- Prepare the Potatoes: Start by giving your potatoes a good wash. Dry them off, and then, using your knife, make a small slit in each potato. You will insert the copper and zinc electrodes here.
- Insert Electrode: Into one potato, place the copper coin or strip and push it in halfway. Do the same with the zinc nail in a separate spot on the same potato. This sets up your first cell.
- Prepare the Second Potato: Repeat the previous step with the second potato. This potato will link to the first one, creating a battery chain.
- Connect the Potatoes: Now, connect the copper of the first potato to the zinc of the second potato using an insulated wire. This forms a circuit between the two potatoes.
- Attach the Load: Connect another insulated wire from the free zinc in the second potato to your light bulb or LED. You’ll now connect the final wire from the copper coin in the first potato to the other terminal of your light bulb.
- Light It Up! If all goes well, your light bulb or LED should light up. If it doesn’t, check your connections, and ensure each part is inserted securely.
And there you have it! You’ve just harnessed the power of potatoes to create your very own battery. Feel free to experiment with different types of fruits or vegetables, and see how their outputs compare. It’s all part of the fun!
Also Read This: Dailymotion for Kids Fun Alphabet Songs and Learning Content in One Place
Exploring Dailymotion Videos for Visual Instructions
When it comes to learning how to create electricity from potatoes, sometimes seeing is believing! Dailymotion is a fantastic resource packed with a variety of videos that provide visual instructions to help you understand the process better. These videos can break down complex concepts into digestible steps, making it easier for both kids and adults to grasp the science behind it.
To get started, you can search for keywords like “potato battery tutorial,” “create electricity from potatoes,” or “simple circuits with vegetables” on Dailymotion. Here’s why these videos are incredibly helpful:
- Visual Learning: Watching someone perform the experiment allows you to see each step in action, increasing your chances of success.
- Variety of Approaches: Different creators may have unique takes on the experiment, giving you multiple methods to try out.
- Engagement: The lively presentation styles can make the learning experience enjoyable and engaging, especially for younger audiences.
- Quick Tips: Many videos include handy tips and tricks that aren’t always found in written instructions.
Be sure to look for videos with high views and positive comments, as this often indicates quality content. Also, don’t forget: experimentation is key! If a particular method doesn’t work out, try another one you found. After all, science is all about trial and error, so dive into those Dailymotion resources!
Also Read This: How to Make Starburst Loom Bands with Forks
Potential Applications and Fun Facts
You might be surprised to learn just how versatile those simple potato batteries can be! The concept of generating electricity from potatoes can open doors to various applications in education, DIY projects, and even potential practical uses. Here are a few interesting applications and fun facts about potato-powered electricity:
- Educational Experiments: In classrooms, potato batteries serve as a hands-on experiment to teach students about chemical reactions, circuits, and renewable energy sources.
- DIY Projects: Enthusiasts can use potatoes to power small devices, such as LED lights, making for fun, creative projects that also demonstrate basic electrical principles.
- Science Fairs: Stand out at your local science fair by creating an impressive potato battery display. You can even challenge your classmates to create batteries from other fruits or vegetables!
- Sustainability Learning: Discussions about using organic materials for generating electricity can lead to more extensive conversations about sustainability and renewable energy sources.
Fun Fact: Did you know that the potato battery was invented back in 1800? Italian scientist Alessandro Volta created the first electrochemical cell using a potato! This experimentation has evolved, but the core principles remain the same.
So, dive into your potato experiment with excitement, and remember—every potato-powered project is an opportunity to learn something new!
Create Electricity from Potatoes with Easy Dailymotion Videos
Creating electricity from potatoes is a fascinating and educational experiment that demonstrates the principles of electrochemistry. Leveraging the natural starch and moisture content found in potatoes, you can generate a small amount of electrical energy using simple materials. This engaging project not only provides insight into how chemical reactions can produce electricity but also makes learning fun and interactive. In this post, we’ll explore how you can create your own potato battery by following a few easy Dailymotion videos.
Materials Required
- Potatoes (2 or more)
- Galvanized nails (zinc-coated, 2 for each potato)
- Copper coins or wires (2 for each potato)
- Electrical wires
- LED light or small digital clock (to demonstrate the power)
Steps to Create Your Potato Battery
- Insert a galvanized nail into one side of each potato.
- Insert a copper coin or wire into the opposite side of the potato.
- Connect one wire from the galvanized nail of potato A to the copper coin of potato B.
- Connect another wire from the copper coin of potato A to the positive terminal of your LED light or digital clock.
- Finally, connect the remaining copper wire from the negative terminal of the LED light or digital clock to the galvanized nail in potato B.
Watch & Learn
For detailed guidance, check out the Dailymotion videos available that showcase step-by-step instructions on creating your own potato battery. These videos make the process clear and enjoyable, catering to various learning styles.
In conclusion, creating electricity from potatoes is not only an exciting science experiment but also a great way to understand fundamental energy concepts. By following along with Dailymotion videos, you can easily replicate this experiment at home or in a classroom setting.
 admin
admin








