Digitizing an image means converting a physical image into a digital format that can be easily stored, edited, and shared. With the rise of digital technology, digitizing images has become a common practice for photographers, designers, and anyone looking to preserve or share their artwork. Whether you're turning a scanned photo into a digital file or capturing an artwork with your smartphone, the process is all about creating a digital version of something physical.
This process opens up many opportunities for editing, organizing, and even sharing images online. With the right tools and techniques, you can easily digitize your photos or drawings with great results. In this guide, we'll walk through the basics of image digitization, explore the most popular methods, and help you choose the right approach for your needs.
Understanding the Basics of Image Digitization
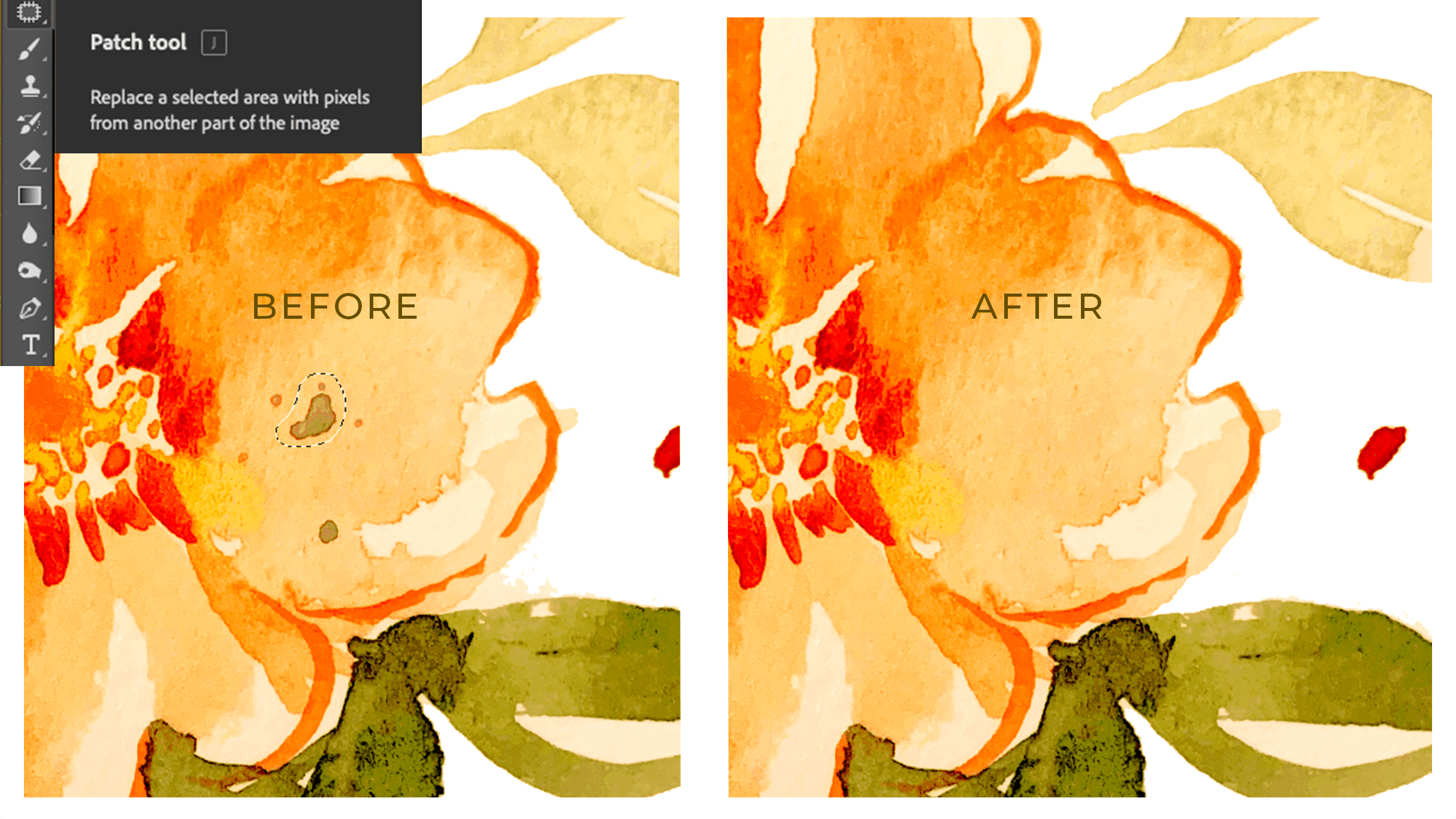
When you digitize an image, you're essentially turning a physical image into a digital file that your computer can read. This allows for easier manipulation, storage, and sharing of the
Here are the basics of how the process works:
- Scanning: Scanners use light sensors to capture the image on a piece of paper or artwork. The scanned image is then converted into a digital format (such as JPEG, PNG, or TIFF) that can be stored on your computer.
- Photography: With this method, you capture an image using a digital camera or smartphone. The image is then transferred to your computer, and you can edit or share it as needed.
Both methods have their own strengths. Scanning is typically used for flat images like photos or drawings, while photography is great for larger or three-dimensional objects. The choice between the two depends on what you need to digitize and the level of detail you're aiming for.
Also Read This: How to Convert Dailymotion Videos Online Easily
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Image

Not all images are created equal, and neither are the methods for digitizing them. The right technique depends on the type of image you're working with, the level of detail needed, and your equipment. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common techniques to help you make the best choice for your project:
- Flatbed Scanning: Ideal for scanning photos, drawings, or documents, flatbed scanners offer high resolution and precise details. This is a great option for images that need high-quality digitization.
- Mobile Scanning Apps: If you don’t have access to a traditional scanner, mobile scanning apps can turn your smartphone into a scanner. These apps are great for quick, everyday digitization, though they may not provide the same level of quality as dedicated scanners.
- Photography: For larger images or items that can’t be easily scanned (like three-dimensional objects or large artwork), using a digital camera or smartphone is an excellent choice. Just make sure the lighting is good, and the camera settings are adjusted for sharpness and clarity.
- Online Tools: Some online tools, like Flaticon downloader, allow you to download images directly from the web, turning them into digital formats that can be used in design work. These tools are perfect for users who need fast access to digital files without scanning or photographing them yourself.
To make your decision easier, ask yourself a few questions:
- Is the image flat or three-dimensional?
- What level of detail do you need?
- Do you have the right equipment for scanning or photography?
- How much time do you have to complete the process?
By considering these factors, you'll be able to choose the method that gives you the best results for your image digitization needs.
Also Read This: how to copy an image from a web page
How to Digitize Images Using Scanners
Scanning is one of the most reliable and popular methods for digitizing images. It involves using a scanner to capture a high-resolution digital version of a physical image. Whether you’re scanning photos, artwork, or documents, this method provides excellent detail and color accuracy, making it a favorite for professional-quality digitization.
Here's how you can get the best results when scanning your images:
- Choose the Right Scanner: There are two main types of scanners: flatbed and sheet-fed. Flatbed scanners are great for photos, documents, and artwork because they allow you to place the image flat on a surface. Sheet-fed scanners, on the other hand, work best for documents that can be fed through the machine.
- Set the Right Resolution: The resolution you choose affects the quality of the scan. For photos, aim for a resolution of at least 300 dpi (dots per inch) for sharp, detailed scans. Higher resolutions (600 dpi or more) are better for capturing fine details in artwork or small text.
- Adjust the Color Settings: Ensure that your scanner is set to capture accurate colors, especially if you're working with photographs or artwork. Most scanners have color calibration options that can help you get the best results.
- Position the Image Properly: Make sure the image is positioned flat on the scanner bed to avoid distortion. If you're scanning a large document or piece of artwork, be mindful of how it fits on the scanner.
Once scanned, your image will be saved as a digital file that can be edited, stored, or shared. This method ensures that you capture every detail of the original, making it ideal for archiving precious photos or creating digital versions of artwork.
Also Read This: How to Monetize on Rumble: A Comprehensive Guide for Creators
Using a Camera to Digitize Images
Using a camera, whether it's a DSLR or a smartphone, is a great alternative to scanning, especially for larger images or objects that cannot fit into a scanner. This method is often quicker and more convenient, but it does require a little more attention to detail to ensure the image is captured correctly.
Here’s how to digitize images with a camera:
- Lighting is Key: Proper lighting is critical when photographing an image to digitize. Natural light is best, but if you're indoors, use soft lighting to avoid shadows or glare. Position the image in a well-lit area to capture the most accurate colors.
- Stabilize the Camera: To avoid blurry images, make sure your camera is stable. Use a tripod if possible, or place the camera on a steady surface. This will help you get sharp, clear images.
- Set the Right Focus: Adjust your camera settings to ensure the image is in focus. If you're using a smartphone, tap on the screen to focus on the subject. If you're using a DSLR, choose a smaller aperture for a greater depth of field.
- Frame the Image Correctly: Ensure the entire image is in the frame and aligned properly. Take the photo directly above the image to avoid distortion.
- Adjust Camera Settings: If you're using a camera with adjustable settings, set it to a higher resolution or use RAW format for maximum detail. This will help capture more detail in your image, especially in areas like textures or fine lines.
Once you've taken your photo, transfer the image to your computer for editing or storage. Using a camera gives you flexibility in capturing large or three-dimensional objects that would be difficult to scan, making it an ideal option for certain types of digitization.
Also Read This: How to Fade Images in Canva for a Soft Effect
Popular Online Tools for Image Digitization
If you’re looking for a fast and easy way to digitize images, online tools are an excellent option. Many of these tools let you convert physical images into digital formats without needing a scanner or camera. These tools are especially useful for quick edits, downloads, or converting existing image files to different formats.
Here are some popular online tools you can use for image digitization:
- Flaticon Downloader: If you're looking for icons or vector images, the Flaticon Downloader is a great tool. It allows you to easily download high-quality icons that can be used in your design projects. These icons are already in digital format, making it a perfect tool for quick access to images.
- Online OCR Tools: Online Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tools, like OnlineOCR or Convertio, allow you to upload scanned images or PDFs and convert them into editable text or other file formats. These are great if you’re looking to digitize documents or images with text.
- Pixlr: Pixlr is a powerful online image editor that also allows you to create or modify images directly in your browser. While not specifically for scanning, it's a great tool to digitize and edit images you’ve taken with a camera or downloaded from other sources.
- Canva: Canva offers a variety of tools to edit and convert images online. You can upload photos and artwork, then use its features to enhance or transform them into digital designs, ready for use in presentations, websites, or social media.
These online tools provide a quick, accessible way to handle your image digitization needs without requiring special equipment or software. Whether you need to download icons, edit images, or convert file types, these tools can save you time and effort.
Also Read This: how do you copy an image from a website
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Digitizing images can be a straightforward process, but there are a few common challenges that can arise. Whether you're scanning photos, photographing artwork, or using online tools, understanding these challenges and how to tackle them will help you achieve the best results. Below are some of the most frequent issues and tips on how to overcome them.
- Low Image Quality: One of the biggest challenges in digitization is poor image quality. This can occur when the resolution is too low or the original image isn’t clear. To avoid this, always use a high-resolution setting when scanning or photographing your image. For scanned images, aim for at least 300 dpi, and for photography, use the highest setting on your camera.
- Color Distortion: Sometimes, digitized images may not match the original color tones. This can happen due to poor lighting when photographing or incorrect color calibration on your scanner. Ensure you’re using natural light when photographing and check the color settings on your scanner before digitizing images.
- File Size Issues: High-quality images can result in large file sizes, making them difficult to store or share. To address this, consider compressing the file without losing quality, or saving it in a more efficient format like JPEG. You can also use online tools to resize or reduce the resolution of your images without compromising too much on detail.
- Distortion from Scanning or Photography: Distortion can occur if the image is not placed correctly on the scanner or if the camera angle is off. Ensure that the image is aligned properly and use a flat surface for scanning. For photos, position the camera directly above the subject and avoid using flash to reduce glare.
By taking a little extra time to address these challenges, you can digitize images with ease and ensure that the quality of your digital file is as close to the original as possible.
Also Read This: Designing a Professional Watermark for Your YouTube Channel
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Method for Your Needs
When it comes to digitizing images, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The best method for you depends on the type of image you’re working with, the tools you have available, and the level of quality you need. Whether you opt for a scanner, camera, or online tool, each approach offers its own benefits and challenges.
To help you make the right decision, consider the following:
- For Flat Images (Photos, Documents, Artwork): A scanner is usually the best option for high-quality results, especially if you need precise details and accurate color.
- For Larger or Three-Dimensional Objects: Using a camera can be a faster, more practical solution, especially for items that won’t fit in a scanner. Just ensure proper lighting and stabilization for the best results.
- For Quick Conversions or Icons: Online tools can be a great choice if you’re looking for speed and convenience. Tools like Flaticon Downloader allow you to access ready-made digital images quickly, without needing to scan or photograph anything yourself.
Ultimately, the key is to choose the method that best suits your needs. If you need high-quality, detailed images, scanning is probably your best bet. For convenience and speed, photography or online tools may be more appropriate. Weigh your options carefully, and you'll be able to digitize images with ease and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about image digitization, along with helpful answers:
- What file format should I choose for my digitized images? The best file format depends on your needs. JPEG is a great option for general use due to its balance of quality and file size. PNG is better for images with transparency, and TIFF is ideal for high-quality scans or professional use.
- How do I ensure the best color accuracy when digitizing images? Use color calibration tools to adjust your scanner or camera settings. Additionally, make sure you’re using proper lighting (preferably natural light) to minimize color distortion.
- Can I digitize large images or artwork that won’t fit in a scanner? Yes! You can photograph large artwork or objects with a camera. Ensure that the image is well-lit, the camera is steady, and the photo is in focus for the best results.
- Why is my scanned image blurry? Blurriness can be caused by a low resolution, poor alignment on the scanner bed, or a dirty scanner lens. Always scan at a higher resolution (300 dpi or more), and make sure your image is placed flat on the scanner.
- Are online tools reliable for digitizing images? Yes, online tools like Flaticon Downloader are useful for quickly downloading and converting images from the web. However, they may not offer the same level of quality as a professional scan or photograph, especially for detailed or high-resolution work.
These answers should help clear up any confusion and guide you toward the best method for your image digitization needs!

 admin
admin








