Inkscape is a powerful vector graphic editor that allows users to create and edit images with precision. While it's known for its vector capabilities, it also offers a variety of tools for cropping and editing raster images. Cropping images in Inkscape may seem a bit different from other image editors, but once you understand the basics, it's a straightforward process. Whether you're trimming edges, removing unwanted sections, or focusing on specific details, Inkscape has the tools to help you achieve the results you want.
Understanding the Basics of Inkscape
Before diving into cropping, it’s important to get familiar with Inkscape’s workspace and tools. Inkscape is an open-source program that supports many image formats, including PNG, JPG, and SVG. The software is highly versatile and allows you to work with both vector and raster images. To crop an image, you need to understand how Inkscape handles objects and layers.
In Inkscape, everything you work with is an object, including your images. These objects can be modified, resized, or clipped. Inkscape offers several tools for working with images, such as the selection tool, drawing tools, and the path tool. While vector images are based on paths and shapes, raster images are made up of pixels. Cropping in Inkscape involves manipulating these objects to focus on the desired area of your image.
Some basic Inkscape features to know:
- Selection Tool: Used to select, move, and scale objects.
- Clip Tool: Helps in cutting out parts of images or objects.
- Mask Tool: Used for hiding or revealing parts of an image.
Also Read This: Projecting an Image to Trace Without a Projector
Preparing Your Image for Cropping
Before cropping, it’s important to ensure your image is ready for the task. Preparing the image properly will help you achieve cleaner and more precise results. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting your
- Import the Image: Start by importing your image into Inkscape. You can do this by going to File > Import and selecting the image file from your computer.
- Resize the Image: If your image is too large or too small, use the selection tool to adjust its size. Hold down the Ctrl key to maintain the aspect ratio while resizing.
- Convert Image to Object: If you're working with a raster image (like PNG or JPG), Inkscape treats it as an object. You don’t need to do anything extra for this, but be aware that the image will not be editable in the same way as vector objects.
- Position the Image: Ensure that the image is positioned correctly on the canvas. You can move it around using the selection tool.
Once your image is prepared, you can start using Inkscape’s tools to crop it, whether you’re using the clip or mask method. Make sure your image is the right size and in the correct position to ensure a smooth cropping process.
Also Read This: Discovering Model Names on Adobe Stock
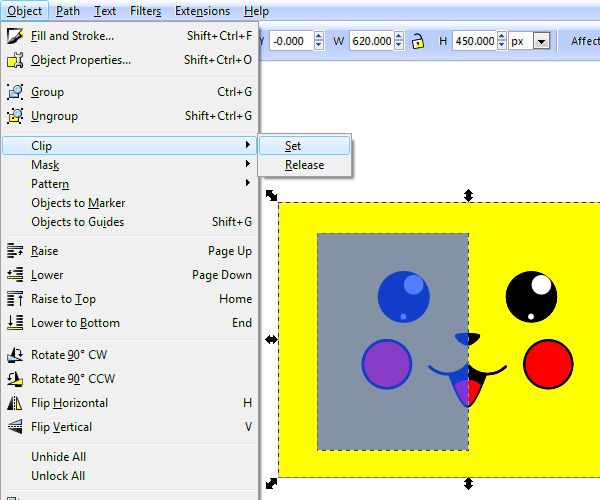
Using the Clip Tool to Crop Images
The Clip Tool in Inkscape is one of the most effective ways to crop images. It works by defining a specific area that you want to keep, while the rest of the image is hidden or removed. This method is ideal for simple cropping tasks, such as cutting away the edges or focusing on a particular section of your image.
Here’s how you can use the Clip Tool:
- Step 1: Create a shape that will act as your cropping mask. For example, you can use a rectangle, circle, or any custom shape you prefer.
- Step 2: Position the shape over the image. The area covered by the shape will be the part of the image that remains visible after cropping.
- Step 3: Select both the image and the shape. You can do this by holding down the Shift key while clicking on both objects.
- Step 4: Apply the clip by right-clicking and selecting Set Clip or using the shortcut Ctrl + 7. This will crop the image to fit the shape you created.
It’s important to remember that the Clip Tool doesn’t delete the parts of the image you crop out. They are simply hidden. If you ever need to bring them back, you can unclip the image by selecting the image and shape and choosing Release Clip.
Also Read This: Calculating Image Distance for Accurate Composition
How to Use the Mask Tool for Image Cropping
The Mask Tool in Inkscape works similarly to the Clip Tool, but with a slight difference: it allows you to control the transparency of parts of your image. Using the Mask Tool is perfect when you want to fade out or make certain areas of an image fully transparent, instead of just cropping them.
Here’s how to use the Mask Tool for cropping:
- Step 1: Create a shape, just like in the Clip Tool method. However, this time, the shape will be used to control the transparency of your image rather than cropping it completely.
- Step 2: Position the shape over the image as needed.
- Step 3: Select both the image and the shape.
- Step 4: Apply the mask by right-clicking and selecting Set Mask or using the shortcut Ctrl + Shift + 7.
The key difference here is that areas of the shape that are white will keep the image visible, while areas of the shape that are black will make the image transparent. Shades of gray will result in varying levels of transparency.
This technique is especially useful for creating soft edges or for blending images into backgrounds in a more natural way. If you need to adjust the mask later, you can easily edit the mask shape or adjust its opacity.
Also Read This: How to Submit My Photos to Getty Images
Adjusting and Fine-Tuning Cropped Images
After cropping your image, you may need to adjust or fine-tune the result to ensure everything looks just right. Inkscape provides a variety of tools to help you tweak the image after the cropping process. Whether you need to make minor adjustments or completely reposition the cropped content, the following steps will guide you through the process.
Here are some adjustments you can make:
- Resizing: If the cropped image doesn’t fit your design, you can easily resize it. Select the image and use the selection tool to adjust the dimensions. Hold the Ctrl key to maintain the aspect ratio while resizing.
- Repositioning: If the cropped image needs to be moved, simply select it and drag it to the desired location. You can use the arrow keys for fine adjustments.
- Rotating: Sometimes a simple rotation is all you need to make your cropped image fit better. Select the image, and then use the rotation handles to rotate it to the right angle.
- Adjusting Opacity: If you want to make the cropped image more subtle in your design, you can adjust its opacity. This is especially useful for images that need to blend with the background.
- Shadows and Effects: You can also add shadows, blur effects, or other visual enhancements to the cropped image. These adjustments can make your image pop or blend seamlessly into your design.
These adjustments ensure that your cropped image not only fits into your project perfectly but also meets your design goals. Don’t be afraid to experiment with these tools until you get the look you want!
Also Read This: Viewing Stereo Images: A Complete Guide
Saving Cropped Images in Inkscape
Once you’ve cropped your image in Inkscape, it’s time to save your work. Saving your cropped image properly ensures that you can use it in other projects or share it with others. Inkscape supports various file formats, including SVG for vector images and PNG or JPG for raster images. Each format has its uses, depending on the type of project you're working on.
Here’s how to save your cropped image in Inkscape:
- Step 1: Once you’re satisfied with your cropped image, go to File > Save As.
- Step 2: Choose the file format you want. For a raster image (like PNG or JPG), you’ll need to export it. For a vector file (like SVG), you can save it directly as a .svg file.
- Step 3: If you’re exporting a raster image, select File > Export PNG Image from the menu. In the Export dialog, choose the desired resolution and export settings.
- Step 4: Name your file and choose the destination folder, then click Save or Export.
Remember that if you’re working with a cropped image in a vector format, you can always adjust or edit it later. For raster images, saving them at a high resolution ensures that the quality remains intact. Inkscape’s export options allow you to tailor the image resolution and other settings for web or print use, so you can get the best quality for your project.
Also Read This: Adding Images in Blender: A Guide
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
While cropping images in Inkscape is usually straightforward, you may encounter a few issues along the way. Understanding these common problems and how to troubleshoot them can save you time and frustration. Here are some of the most frequent challenges you might face when cropping images in Inkscape:
- Image Not Appearing After Cropping: If your image disappears after applying a clip or mask, check if the image layer is hidden or if the transparency is set too high. Make sure the image is in front of the clipping or masking shape.
- Clip or Mask Not Working: Sometimes the clip or mask doesn’t work as expected. Ensure both the image and the shape are selected correctly before applying the clip or mask. If necessary, use the Object > Raise to Top option to bring your image to the front.
- Image Quality Loss: Cropping a raster image might reduce its quality if it’s resized or exported improperly. To avoid this, make sure to save images at a high resolution, and check your export settings to avoid compression.
- Unable to Undo Actions: If you accidentally crop the image too much, and you can’t undo it, it may be helpful to save a backup of the original image. Regularly saving versions can help you avoid losing important work.
- Inkscape Crashing or Freezing: Inkscape can sometimes become unresponsive, especially when working with large files. If this happens, try closing other programs to free up system resources or reduce the image resolution before importing it into Inkscape.
If you encounter these or other issues, take your time troubleshooting by checking the file layers, reapplying the tools, or reviewing your settings. Inkscape’s active community forums and online resources can also provide solutions to more complex problems.
Also Read This: Learn How to Sell Photos to Shutterstock
FAQ
Q1: Can I crop vector images in Inkscape?
Yes! Inkscape is primarily a vector graphics editor, and you can crop vector images using the same methods (Clip and Mask tools) as you would with raster images. You can also adjust paths and shapes directly to modify vector objects.
Q2: Will cropping an image in Inkscape affect its quality?
Cropping an image in Inkscape will not affect the quality unless you resize it or export it at a lower resolution. For the best results, always save your images in the appropriate resolution for your needs.
Q3: How do I bring back parts of an image after clipping it?
If you accidentally clip out too much of the image, you can restore the hidden parts by selecting the clipped image and shape, then clicking Release Clip under the Object menu. This will allow you to adjust the clipping path.
Q4: What file formats can I save my cropped image in?
Inkscape allows you to save your cropped image in several formats, including SVG for vector images and PNG, JPG, or TIFF for raster images. Choose the format that suits your project—raster formats for online or print usage, and vector formats for further editing or scalable designs.
Q5: How can I make the edges of a cropped image softer?
To make the edges of a cropped image softer, you can use the Mask Tool with a gradient or adjust the opacity of the mask shape. This will create a fade effect on the edges, giving your cropped image a more natural and seamless look.
Conclusion
Inkscape offers a powerful set of tools for cropping images, whether you’re working with vector or raster formats. By understanding the basics of Inkscape, preparing your images correctly, and using the Clip and Mask tools, you can easily crop your images to fit your design needs. Adjusting, fine-tuning, and saving your cropped images ensures that they are high-quality and ready for any project. With some practice, you’ll be able to crop images precisely and efficiently, adding professional touches to your work. Remember to troubleshoot any issues by reviewing your settings and exploring Inkscape's wide range of features for image editing.
 admin
admin








